ccna-notes
Interfaces and Cables
Table of contents
- Network Protocols
- Bits and Bytes
- Ethernet
- Cable Standards
- Copper UTP Cables
- Fiber-optic UTP Cables
- UTP vs Fiber-optic Cabling
Network Protocols
Agreed upon system of communicating between network devices.
Bits and Bytes
- Bit =
0or1 - Byte = 8 bits
Speed

Ethernet
Collection of network protocols/standards that fit in RJ-45 ports.
- RJ = “Registered Jack”
Cable Standards
- defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard in 1983
- IEEE = Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Copper UTP Cables
Type of copper cables used in ethernet standards.
Unshielded= no metallic shield, which makes them vulnerable to electrical interferenceTwisted Pair= Literaly 4 pairs of wires with each pair twisted together, protecting against EMI (Electromagnetic Interference)8 pins, perfect for the number of wires-
Not all ethernet cables use all 8 wires

Copper cable standards
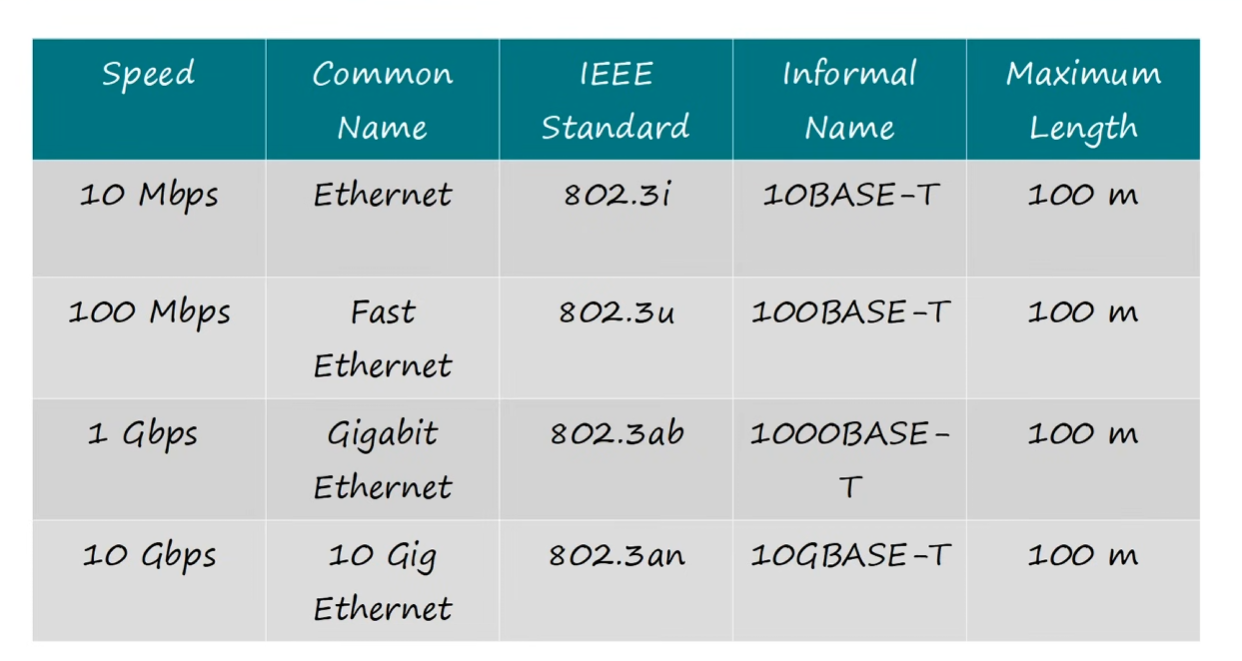
- “BASE” refers to baseband signaling (outside of CCNA scope) and “T” refers to “twisted pair”
10BASE-T and 100BASE-T
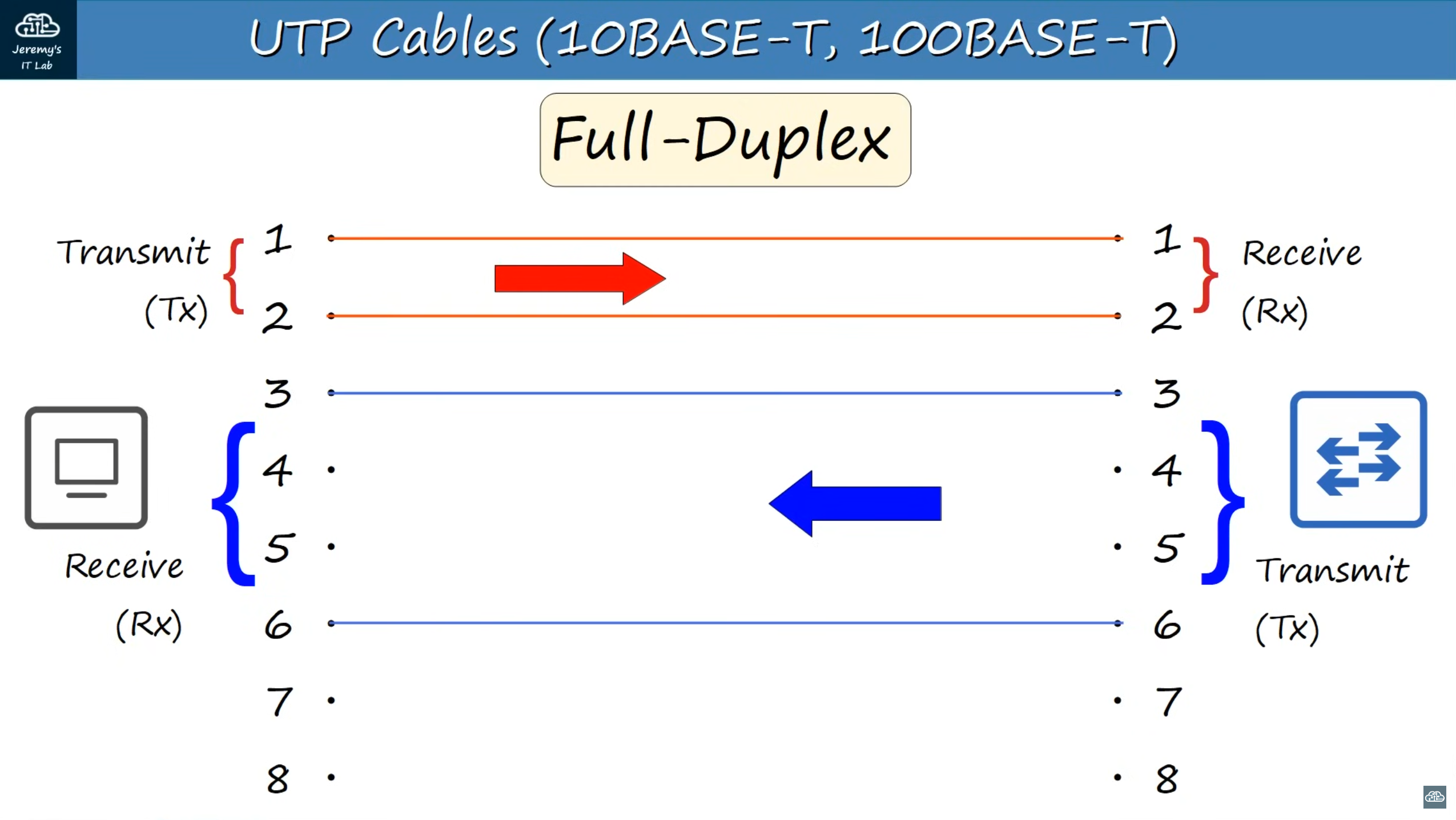
Full-Duplextransmission: both connected devices can receive and transmit data at the same time
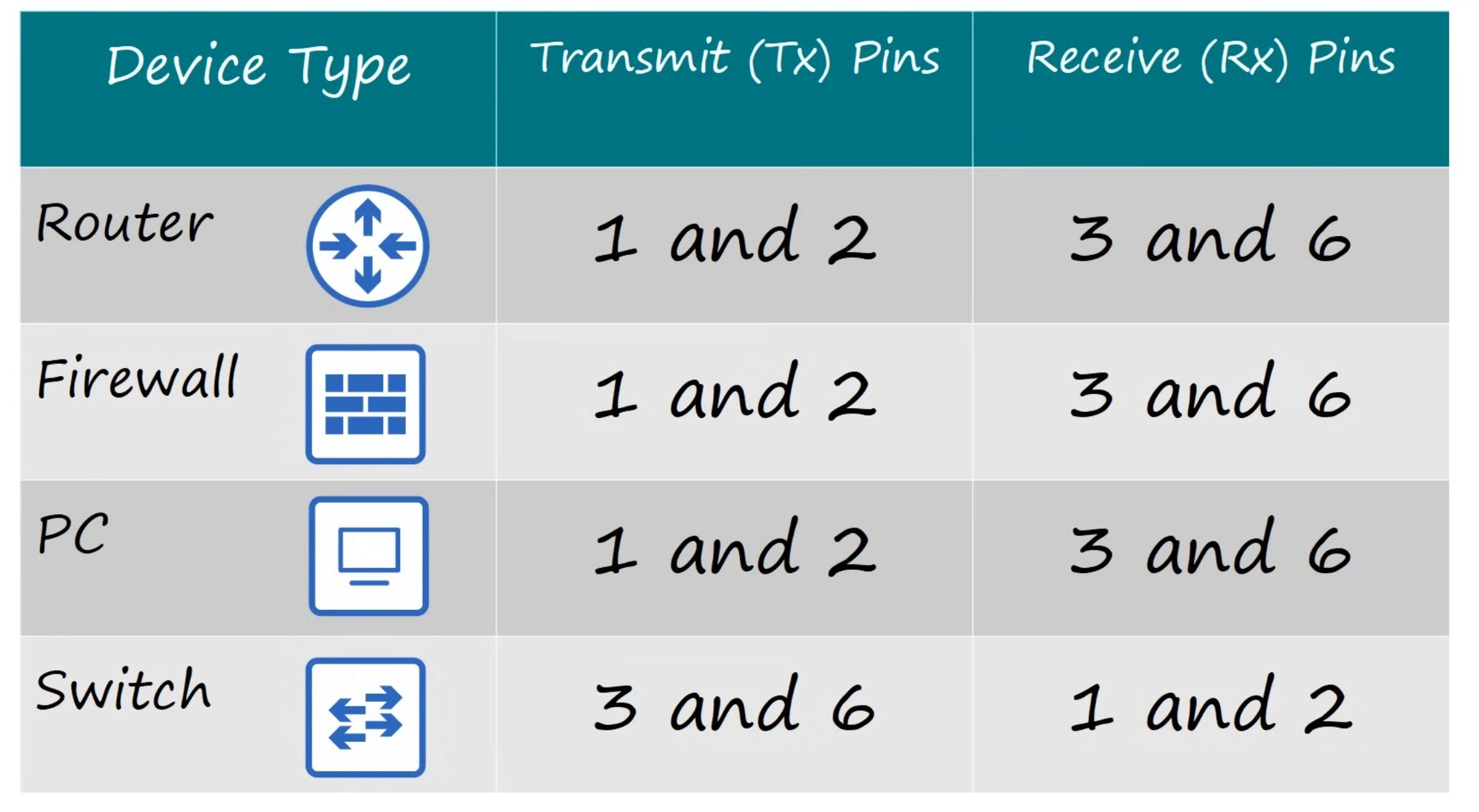
Straight-through cable connections
1 --- 1
2 --- 2
3 --- 3
6 --- 6
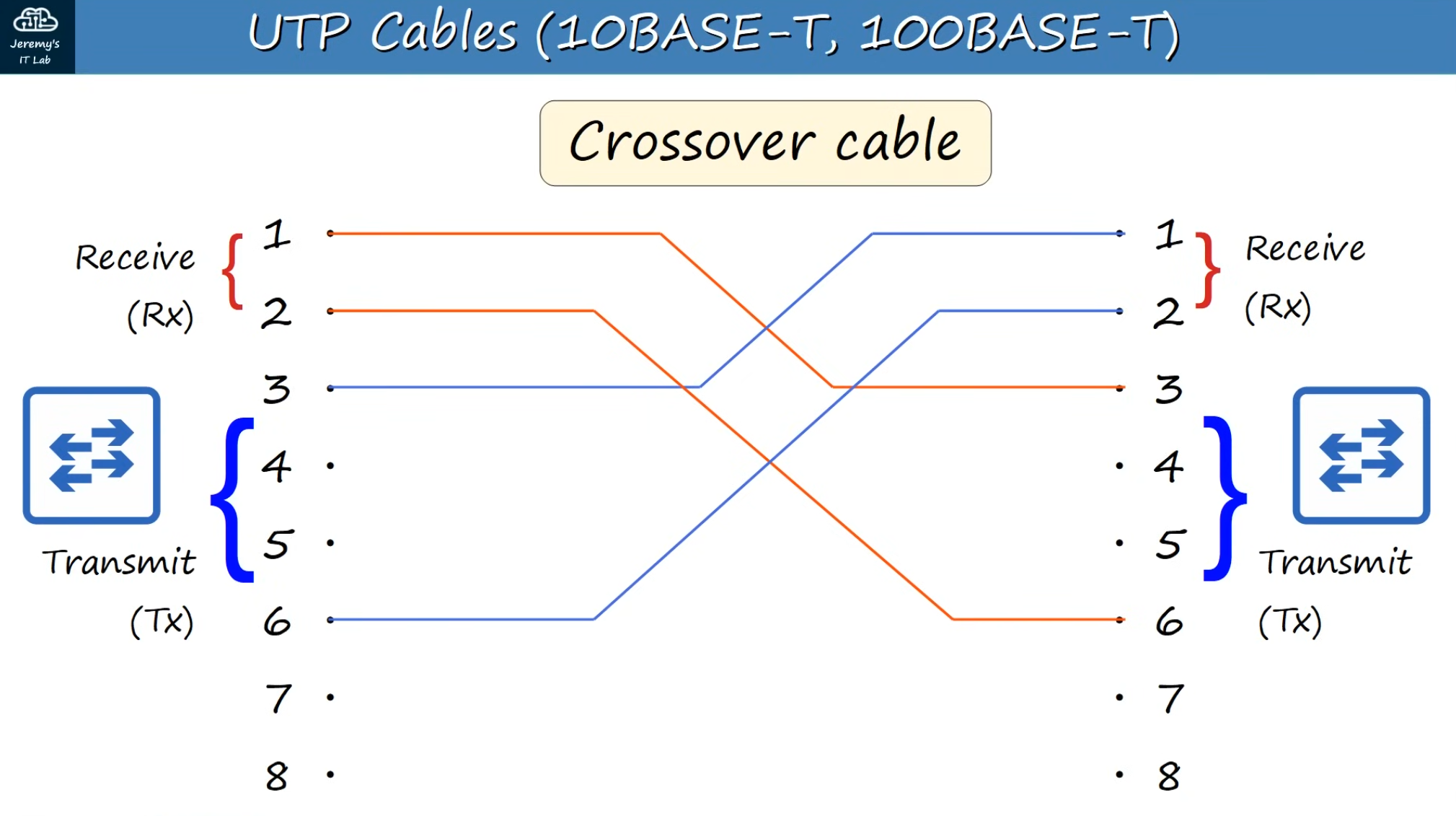
Crossover cable connections
1 --- 3
2 --- 6
3 --- 1
6 --- 2
Auto MDI-X 🔥
Truth is that most modern network devices don’t need to worry about straight-through or crossover cables because of Auto MDI-X.
It allows deviced to automatically detect which pins their neighbor is transmiting data on, and then adjust which pins to use to transmit/receive data.
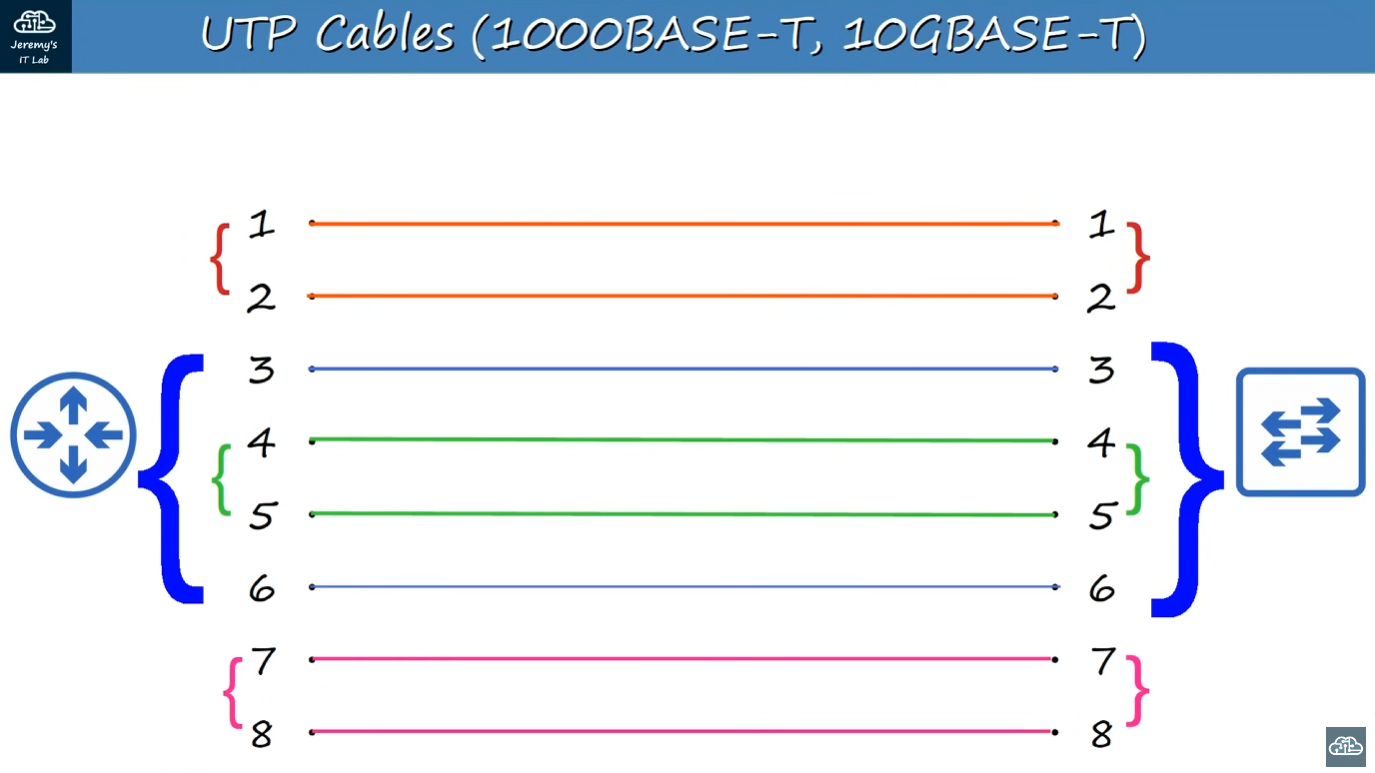
1000BASE-T and 10GBASE-T
In addition to using ALL pairs of wires, each pair is BI-DIRECTIONAL. This is part of the reason why they can operate at much faster speeds.
1 --- 1
2 --- 2
3 --- 3
6 --- 6
4 --- 4
5 --- 5
7 --- 7
8 --- 8
Fiber-optic UTP Cables
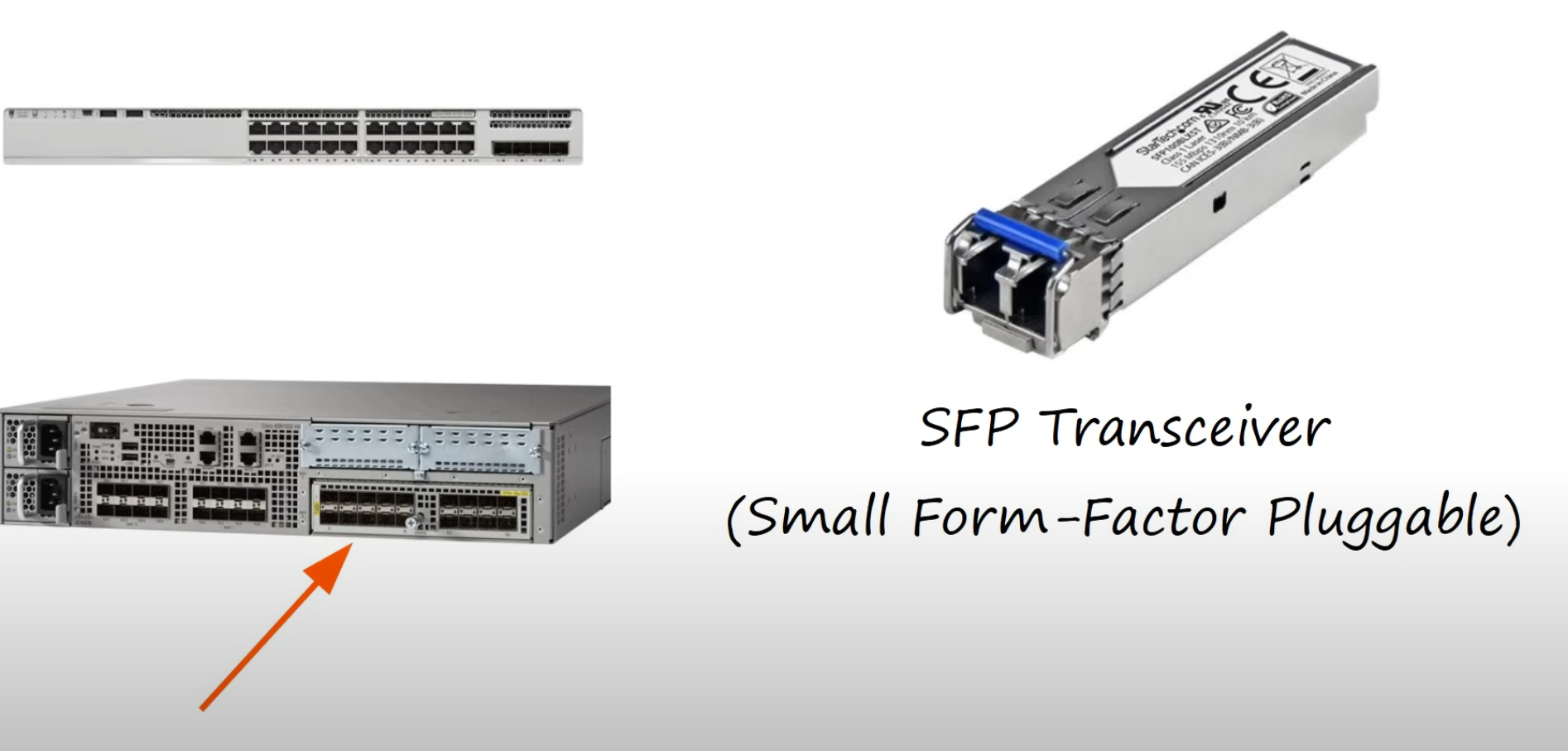
Connections

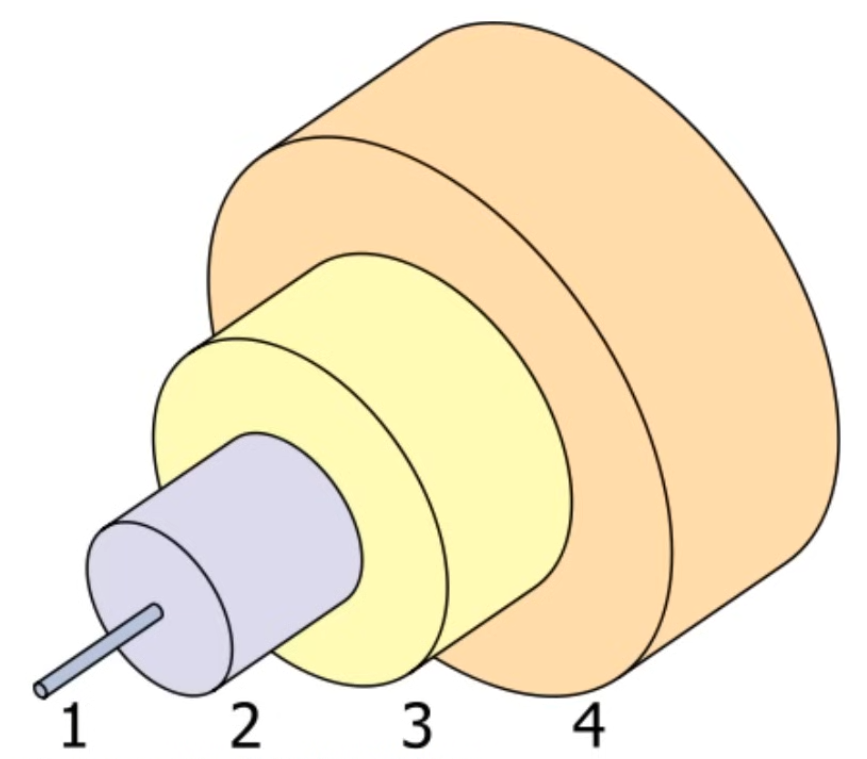
1: Fiber glass core, where light is transmitted2: Cladding that reflects light3: Protective buffer4: Outer jacket of the cable
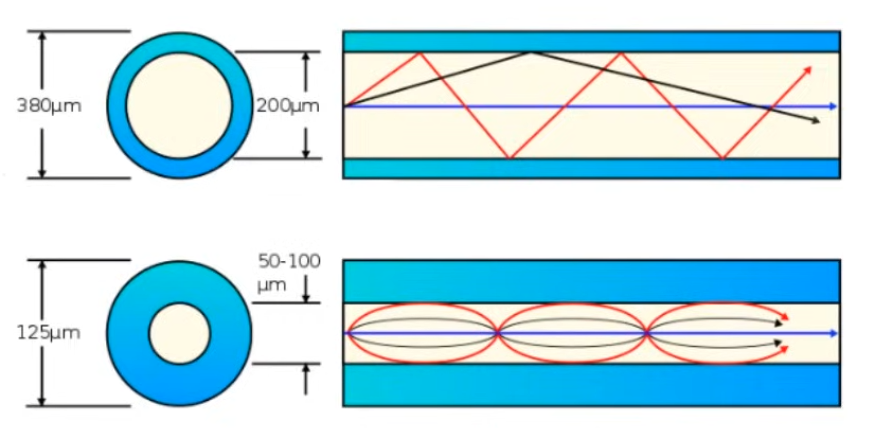
Single-mode
- Narrower core than multimode
- Single angle (mode) from laser-based transmitter
- Allows longer cables than UTP and multimode
- More expensive than multimode fiber (laser-based sfp transmitters)
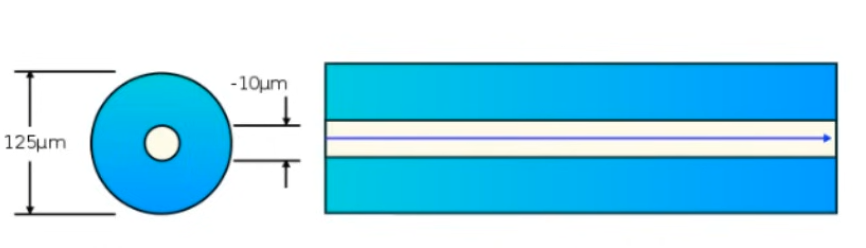
Multimode
- Wider fiber glass core than single-mode fiber
- Allows multiple angles (modes) of light waves to enter the fiber glass core
- Allows longer cables than UTP
- Shorter cables than single-mode fiber
- Cheaper than single-mode fiber (led-based sfp transmitters)
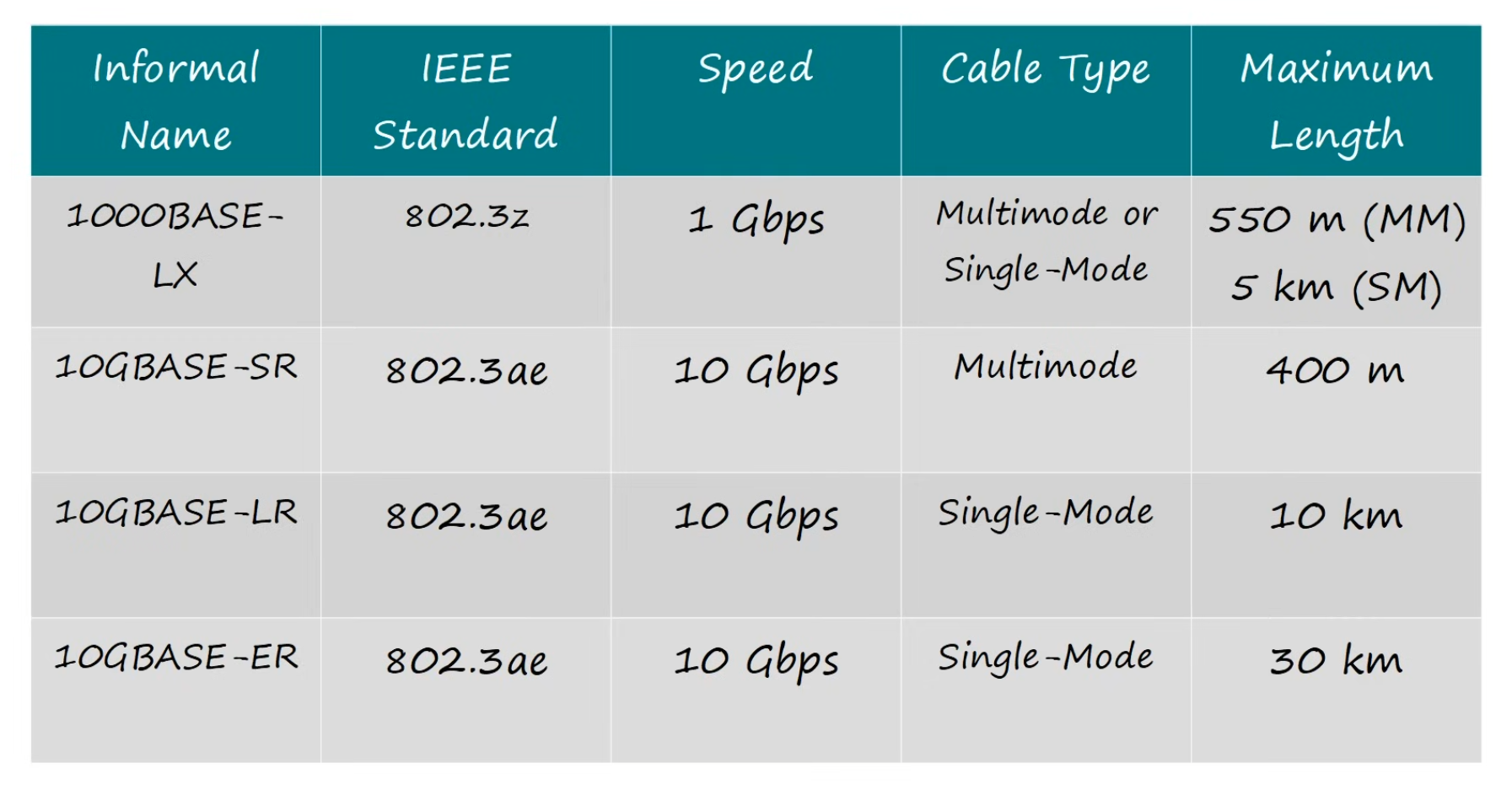
Fiber-optic Cable standards
UTP vs Fiber-optic Cabling
| UTP | Fiber-optic |
|---|---|
| Cheaper | More expensive |
| Shorter max distance (~100m) | Longer max distance |
| Vulnerable to EMI | EMI proof |
| RJ45 ports are cheaper than SFP ports | SFP ports are more expensive (and single-mode ir more expensive than multimode) |
| Leak faint signal outside of cable (security risk) | No signal leak |