ccna-notes
OSI Model and TCP/IP Suite
Table of contents
Networking models
Networking models categorize and provide structure for networking protocols and standards.
OSI Model
Open Systems Interconnection model
- categorizes and standardizes the different functions in a network
- created by the Internatinal Organization for Standardization (ISO)
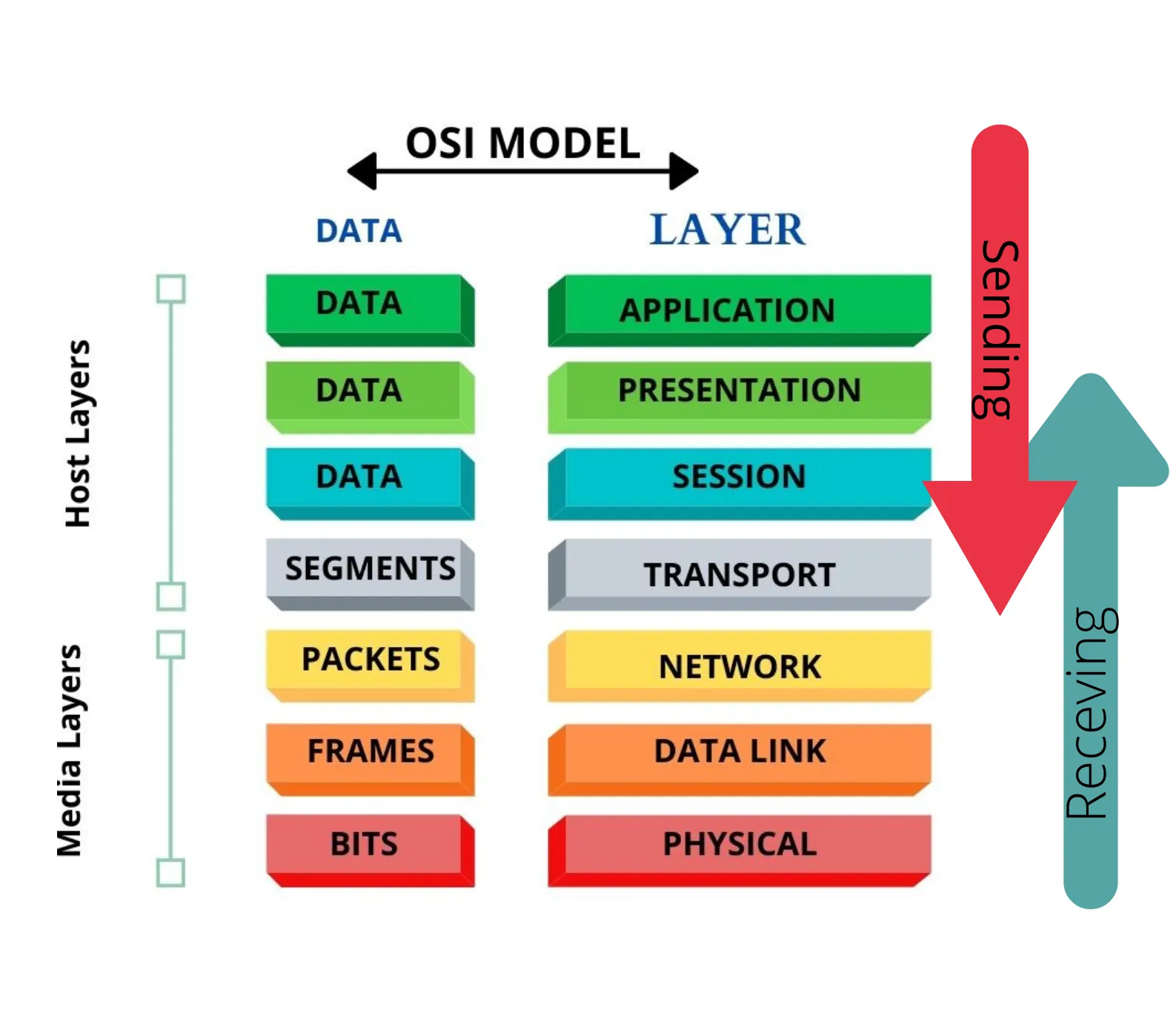
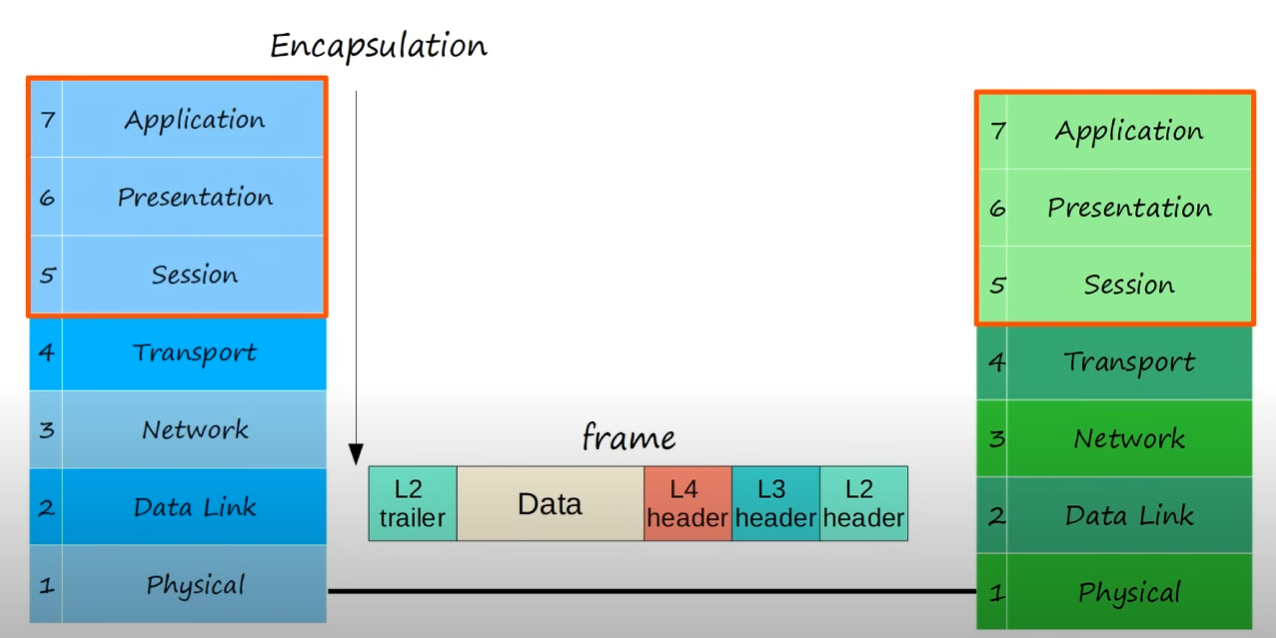
- Functions are divided into 7 layers
- These layers work together to make the network work
L7 - Application
- this layer is the closest to the end user
- interacts with software applications (i.e. browsers)
- serves as the window for users and app processes to access network services
- HTTP and HTTPS are Layer 7 protocols
- identifies communication partners
- synchronizes communication
L6 - Presentation
- translate between application and network formats
- handles encryption and decryption
L5 - Session
- controls dialogues (sessions) between comunication hosts
- establishes, manages and terminates connections between local and remote app
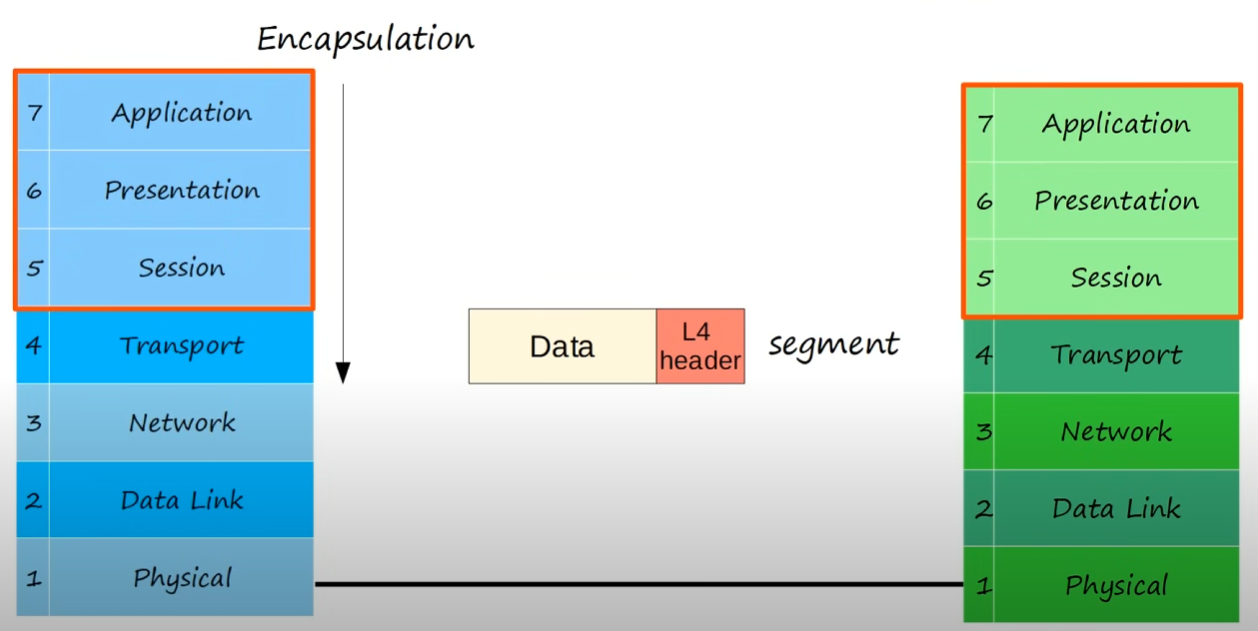
L4 - Transport
- segments and reassembles data for communications between end hosts
- breaks large pieces of data into smaller segments which can be more easily sent over the network and are less likely to cause transmission problems if errors occur
- provides host-to-host communication (end to end, process to process, etc) 🔥
- adds a L4 header to the data from L7/L6/L5 forming a
segment🔥
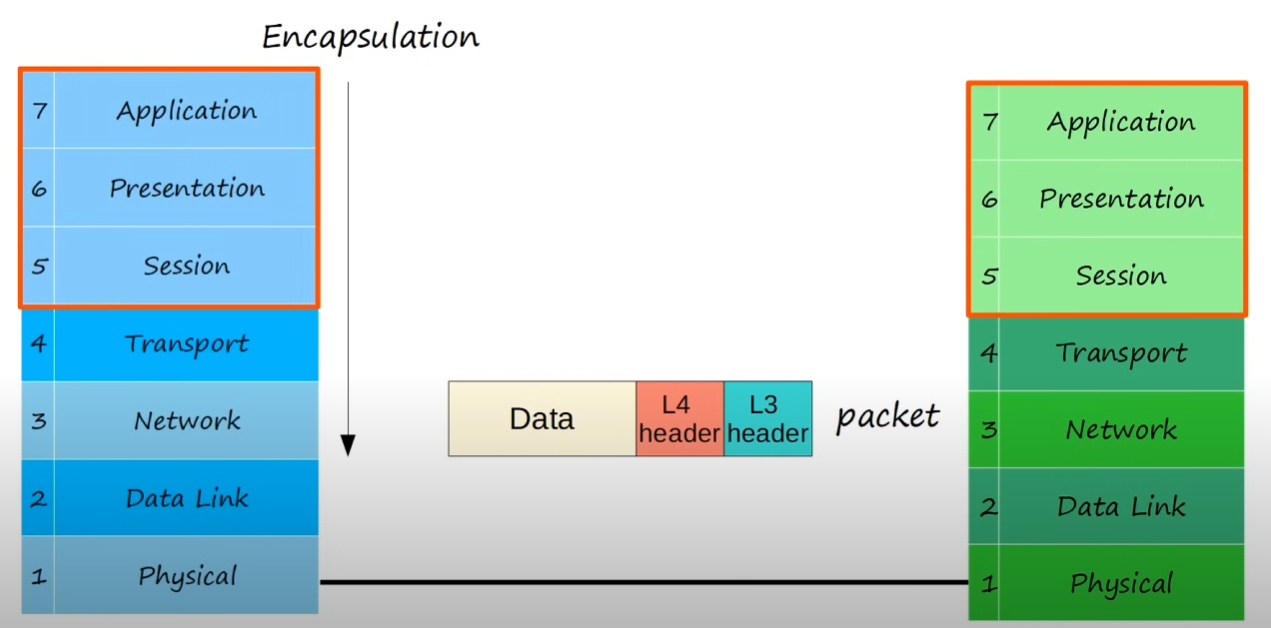
L3 - Network
- provides connectivity between end hosts on different networks
- provides logical addressing (IP addresses)
- controls operations of the subnet, deciding physical path the data takes
- routers operate at Layer 3
- adds a L3 header to the segment from L4 forming a
packet🔥
L2 - Data Link
- provides node-to-node connectivity and data transfer (i.e. PC to switch, switch to router, router to router)
- defines how data is formatted for transmission over physical medium (like copper UTP cable)
- detects and possibly corrects Physical Layer errors
- uses its own L2 addressing, separate from Layer 3 addressing
- switches operate at layer 2
- adds l2 header AND trailer to packet from L3 forming a
frame🔥
L1 - Physical
- defines physical characteristics of the medium used to transfer data between devices (i.e. voltage levels, max tx distances, physical connectors, cable specs, etc)
- digital bits are converted into electrical or radio signals (wired and wireless connections respectively)
- interfaces and cables section of this repo is related to this layer
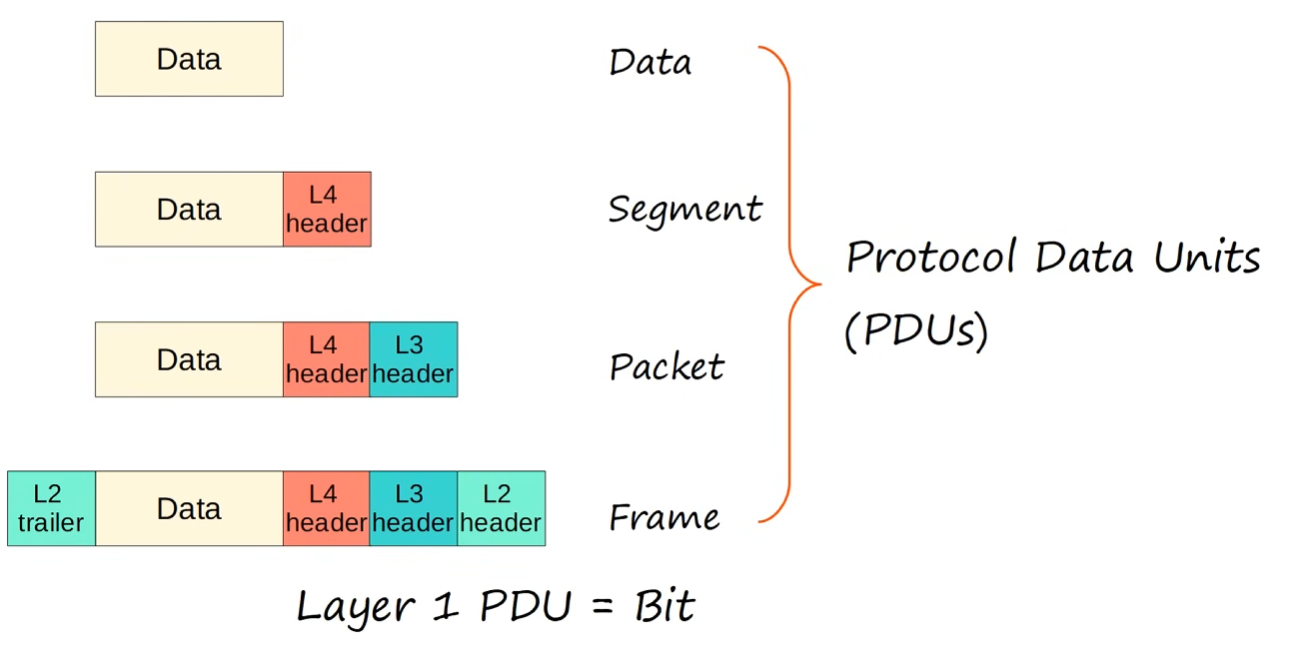
PDUs (Protocol Data Units)
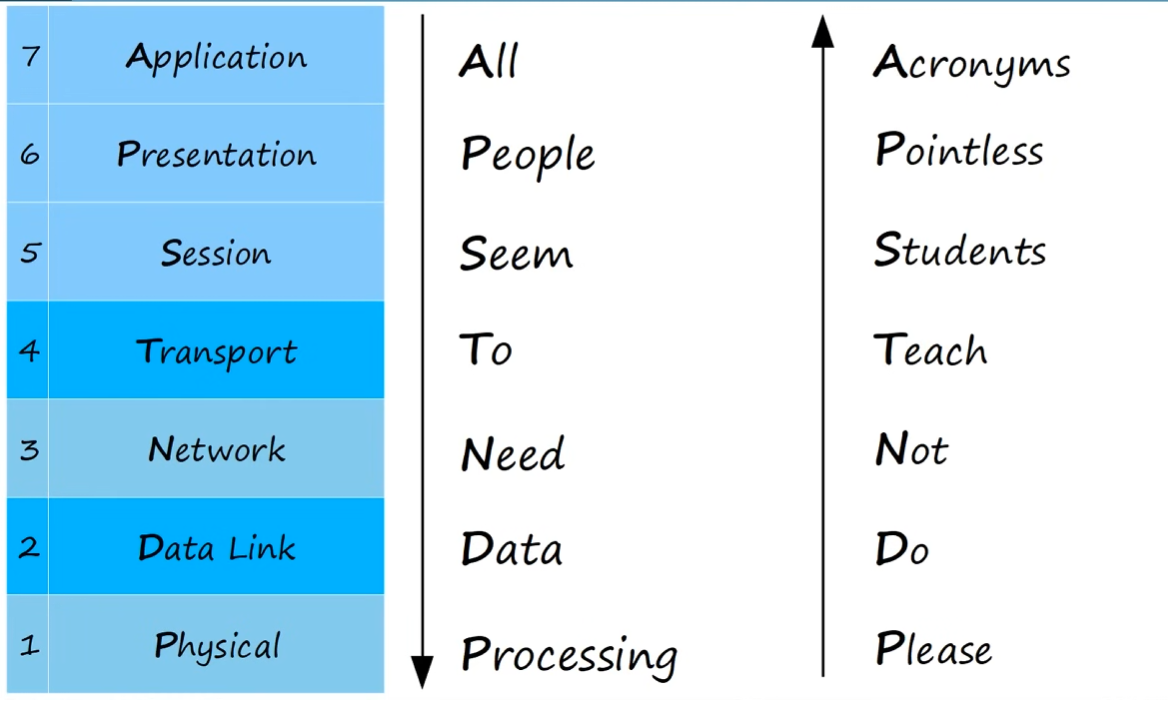
OSI funny acronyms
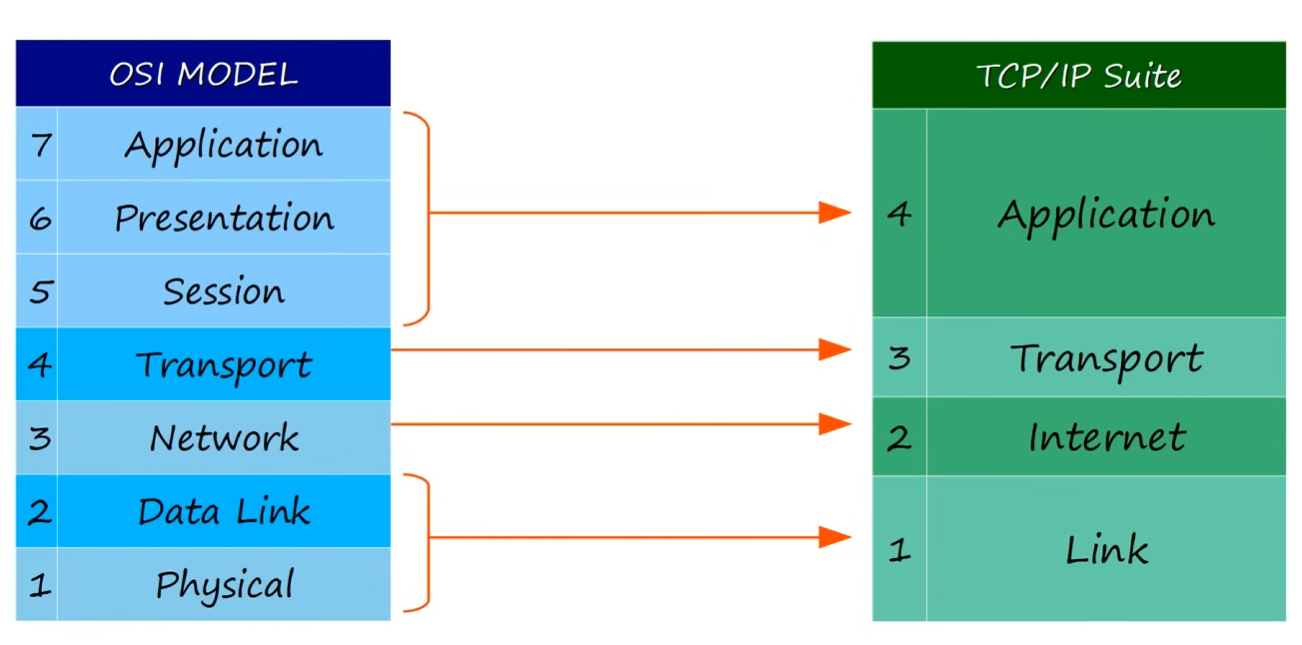
TCP/IP
- used in the internet and other networks today
- known as TCP/IP becuase those are two of the foundational protocols in the suite
- developed by the US Department of Defense through DARPA
- similar to OSI model but with fewer layers