ccna-notes
Routing Fundamentals
Routing is the process that routesrs use to determine the path that IP packets should take over a network to reach their destination. Routers store routes to all of their known destinations in a routing table. When routers receibe packets, they look in the routing table to find the best route to forward that packet.
Table of contents
Routing Methods
There are two main routing methods:
-
Dynamic Routing: routers use dynamic routing protocols (i.e. OSPF) to share routing information with each other automatically and build their routing tables.
-
Static Routing: a network engineer/admin manually configures routes on the router
Routes
A route tells the router to:
- send a packet to destination X, you should send the package to next-hop Y
next-hop= the next router in the path to the destination
- send the packet directly to the destination (if it is directly connected to the router)
- receive the packet for yourself (if the destination is the router’s own IP address)
Routing Tables
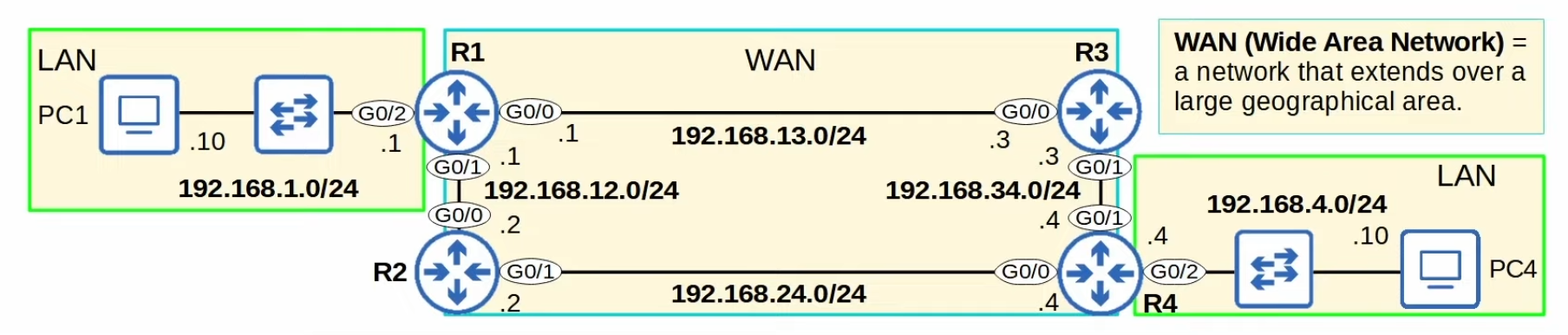
Pre-config
For simplicity we’ll only show R1’s config.
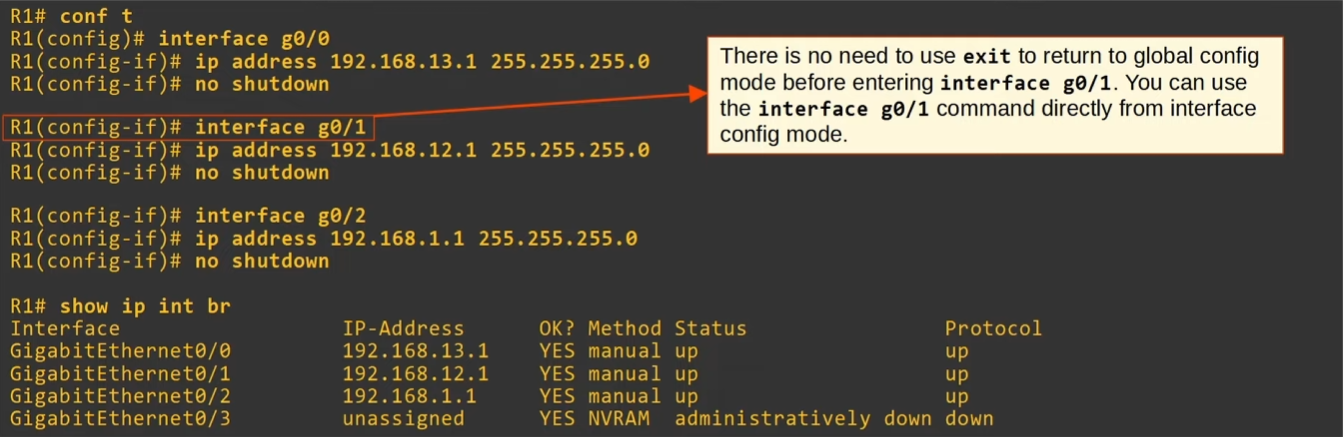
Connected and Local routes
show ip routeto view routing table 🔥
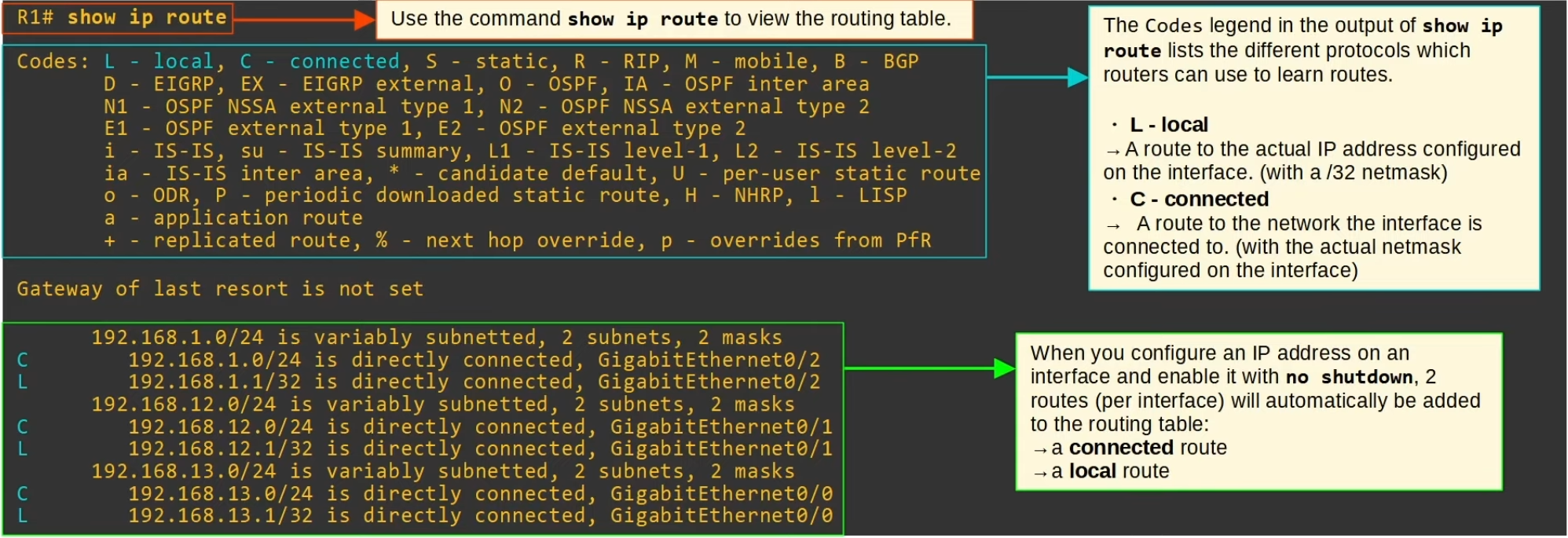
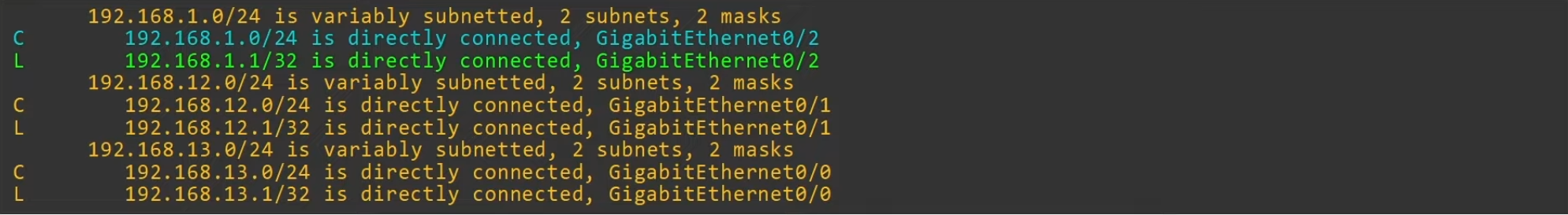
Connected Routes
- Route to the network the interface is connected to
- R1 G0/2 IP =
192.168.1.1/24 - Network address =
192.168.1.0/24 - It provides a route to all hosts in that network (i.e. 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.232, etc)
- R1 knows: “if I need to send a packet to any host in 192.168.1.0/24, I should send it out to
G0/2”
Local Routes
- Route to the exact IP address configured in the interface
/32netmask is used to specify the exact IP address of the interface- Even tough R1’s G0/2 is configured as
192.168.1.1/24, the local route is192.168.1.1/32 - R1 knows: “if I receive a package destined for this IP address, the message is for me”
Route Selection
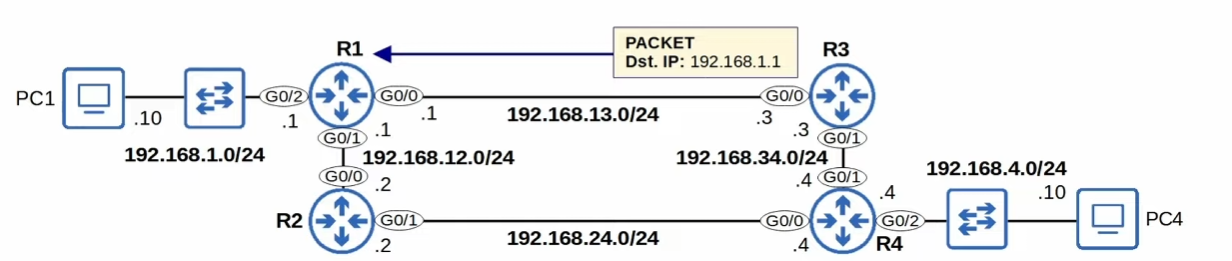
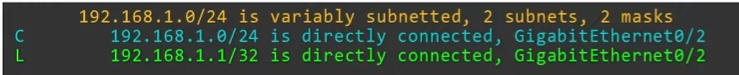
A packet destined for 192.168.1.1 is matched by 2 routes in the example above:
192.168.1.0/24192.168.1.1/32
It will choose the most specific matching route.
- most specific matching route = the matching route with the longest prefix length 🔥