ccna-notes
Switch Interfaces
Configuring interfaces
The following is the network topology we’ll use for this section

show ip interface brief
Running show ip interface brief in privileged EXEC mode will do the trick just like with routers
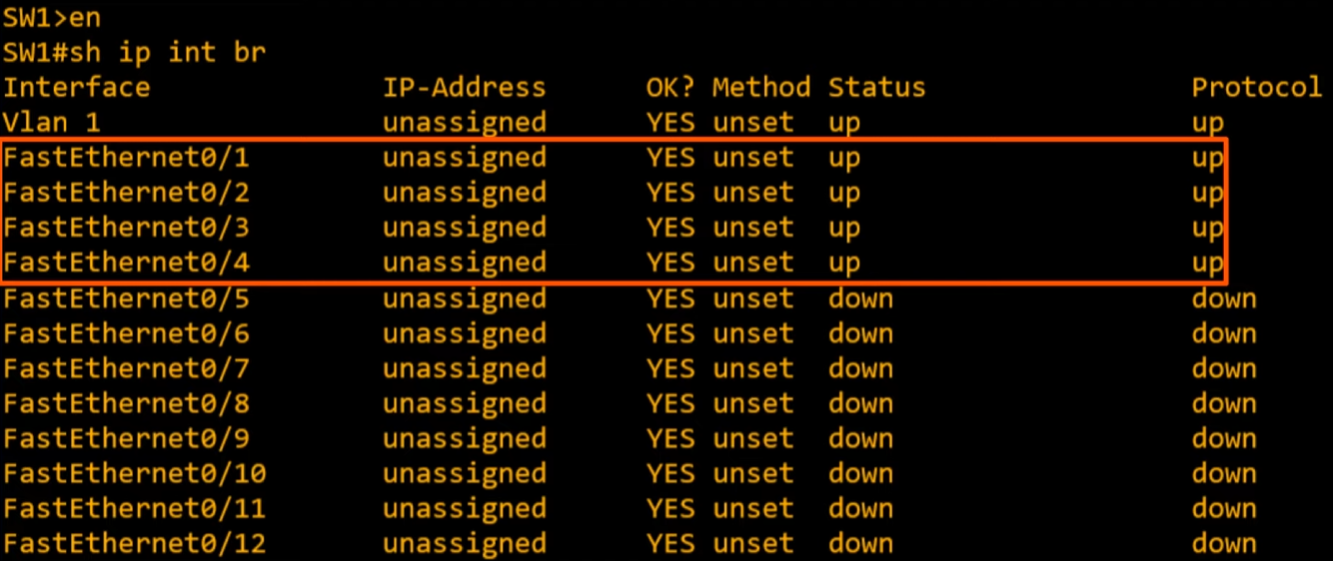
We can already tell a difference between Cisco switches and routers; interfaces do not have the shutdown command applied by default. So if you connect them to another device they will usually be in the status=up and protocol=up state with no configuration required. 🔥
- interfaces not connected to a device will have
status=down and protocol=downstate by default
show interfaces status
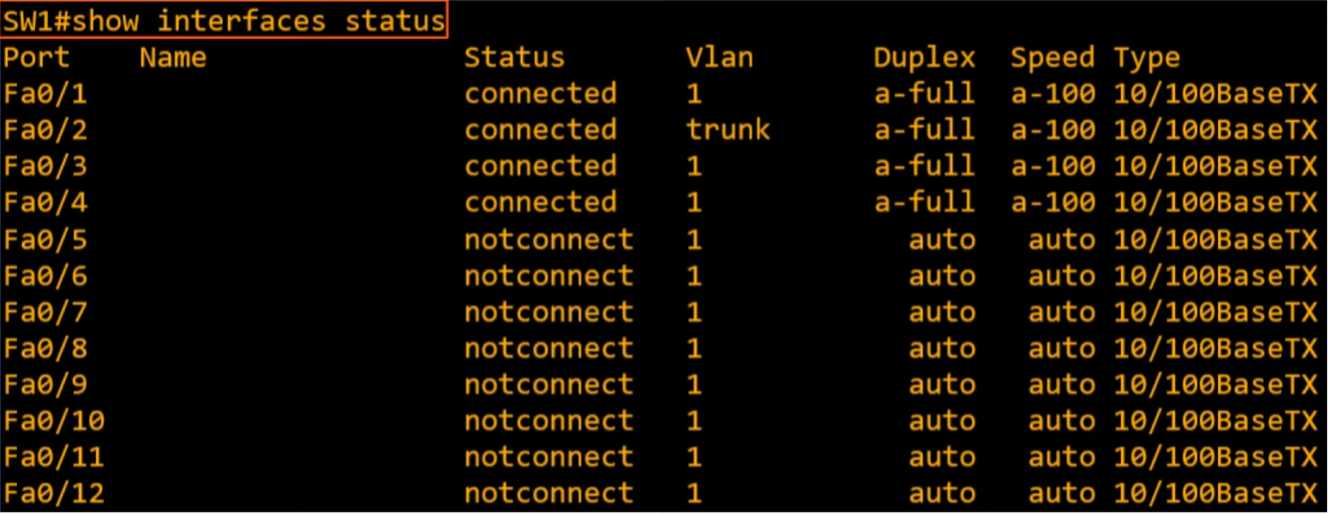
name=descriptionVlan: they can be used to divide LANs into smaller LANs- interface connected to another switch is a trunk interface 🔥
Duplex: indicates whether the device is capable of sending and receiving data at the same time 🔥🔥🔥full duplexwhen capablehalf duplexwhen notduplexisautoby default in Cisco switches. Meaning it will negotiate with neighbor device and use full duplex if possiblea-full: automatically negotiatedfull duplexwith connected device
Speedautoby default. Meaning it will negotiate with neighbor device and use the fastest speed both devices are capable.a-100: automatically negotiated100Mbps
Configuring interface speed and duplex
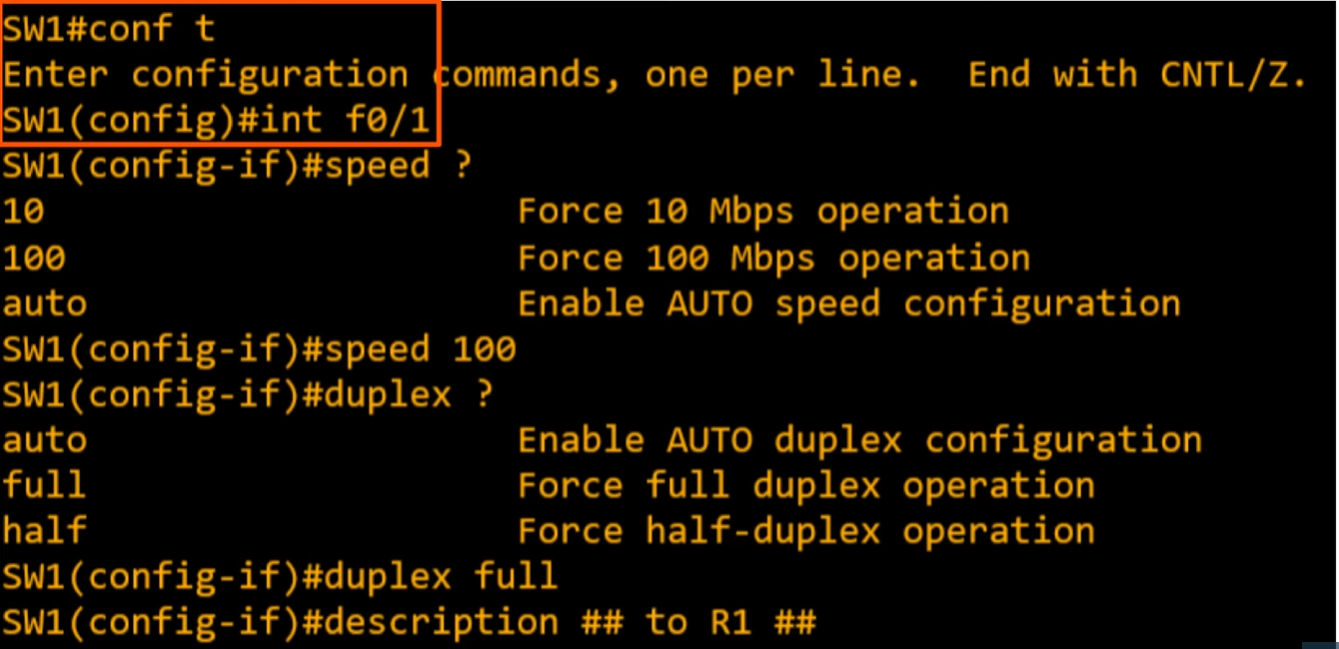
interface f0/1to select f0/1 interfacespeed 100to configure speed to 100Mbpsduplex fullto configure duplex to fulldescription <description>to change thenamefield (description)
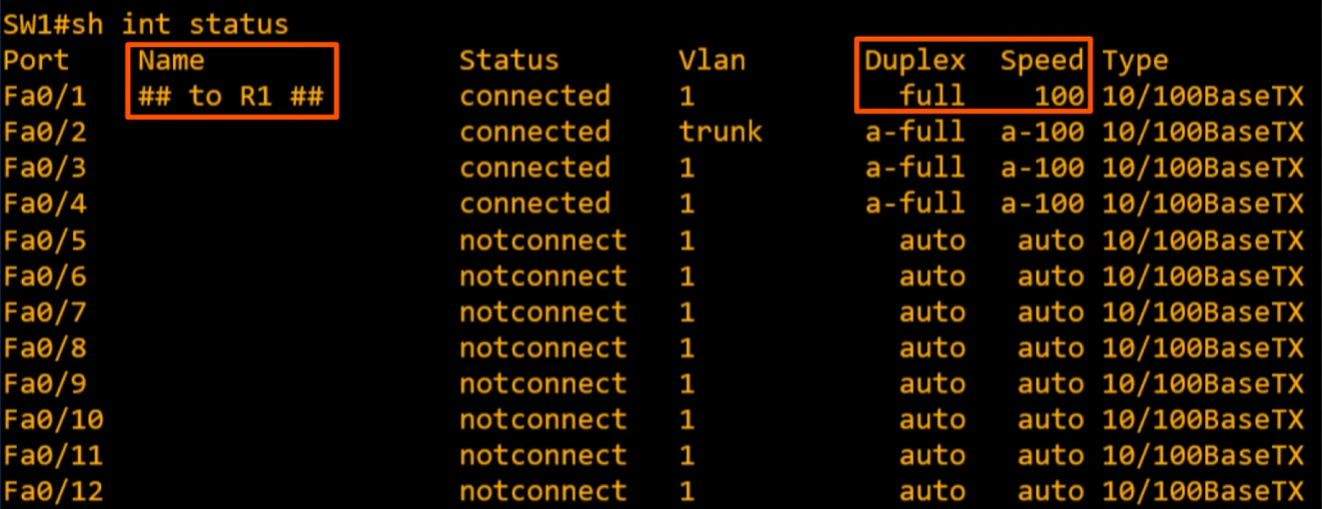
Disabling unused interfaces
For security concerns we should disable the unused interfaces
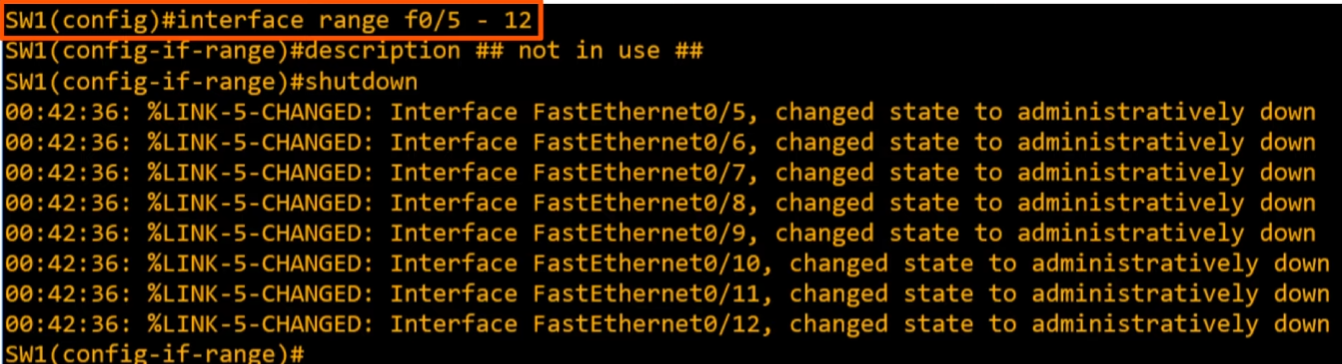
interface range f0/5 - 12to select multiple interfaces at once (f0/5 to f0/12 in this one) 🔥🔥🔥description <description>to change thenamefield (description)shutdownto disable interfaces
Full/Half Duplex
Half Duplex
The device cannot send and receive data at the same time. If it is receiving a frame, it must want before sending a frame.
Half Duplex is pretty much unused in modern networks
LAN Hubs
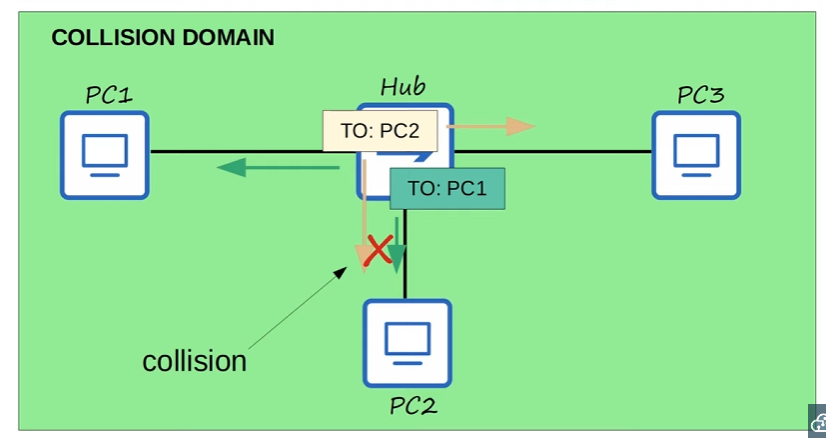
In the past, before network switches, HUBS were used. Hubs acted as a repeater, meaning that any frame it receives is FLOODED. 🔥
-
PC1sends a frame forPC2andPC3sends a frame forPC1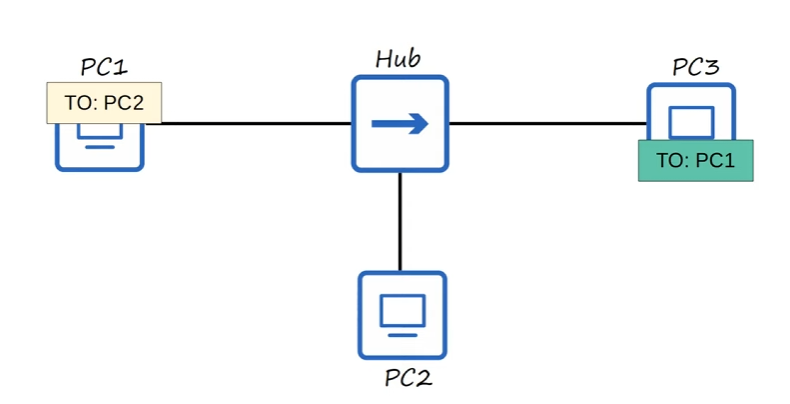
-
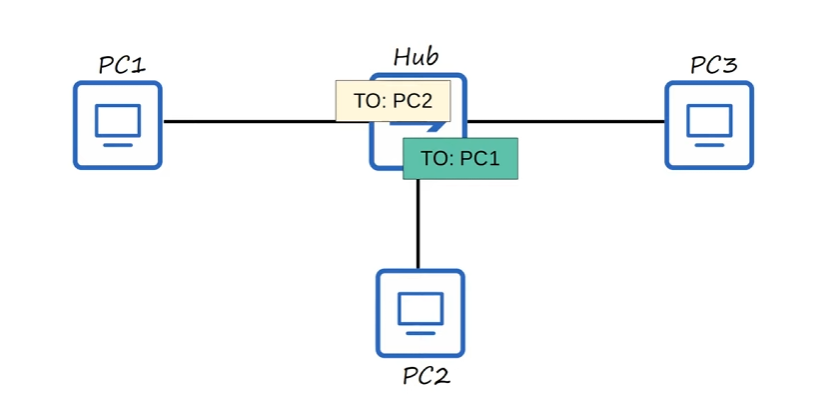
Both frames are sent through their network interfaces
-
The Hub will try to
FLOODboth at the same time resulting in a collision 🔥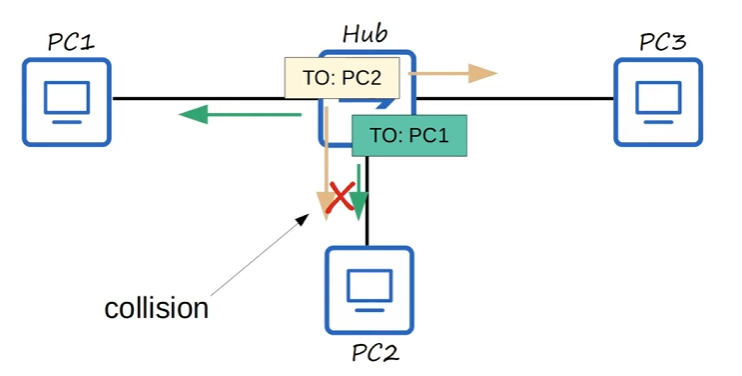
- All devices connected to a Hub are part of something called a Collision Domain
Full Duplex
The device can send and receive data at the same time.
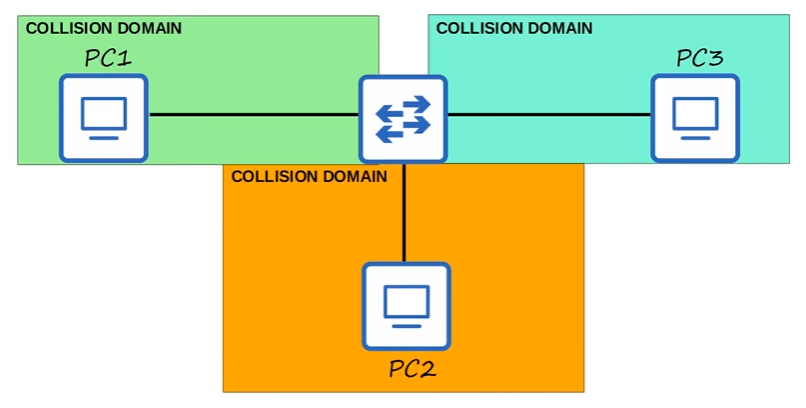
- Because of the improved functionality of Switches over Hubs, each connection to the switch is in its own Collision Domain. This means that devices don’t need to worry about other devices sending data at the same time.
CSMA/CD
To deal with colisions in a half-duplex situation like the one above, ethernet devices use a mechanism called CSMA/CD.
It stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection 🔥
- before sending frames, devices “listen” to the collision domain until they detect that other devices are not sending.
- if a collision does occur, the device sends a jamming signal to inform other devices that a collision happened.
- each device will wait a random period of time before sending frames again
- the process repeats
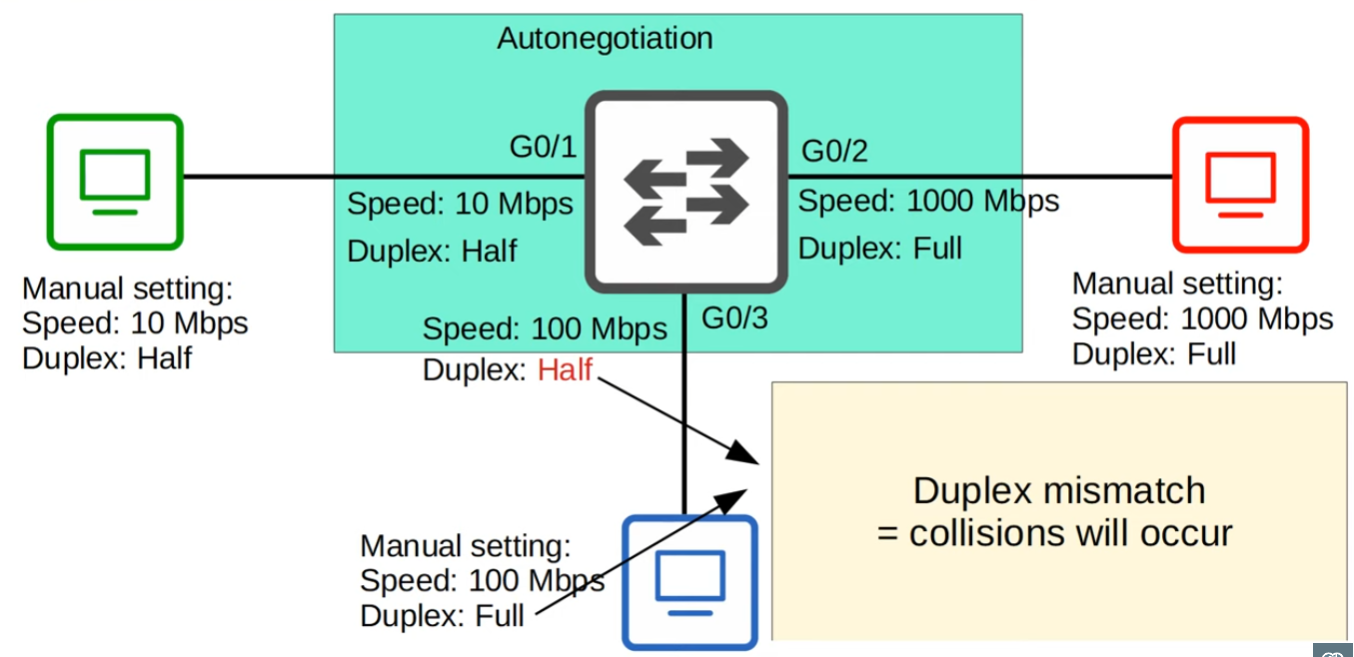
Speed/Duplex Autonegotiation
- interfaces that run on different speeds (10/100 or 10/100/1000) have default settings of speed auto and duplex auto
- interfaces “advertise” their capabilities to the neighboring device, and they negotiate the best speed and duplex settings they are both capable of.
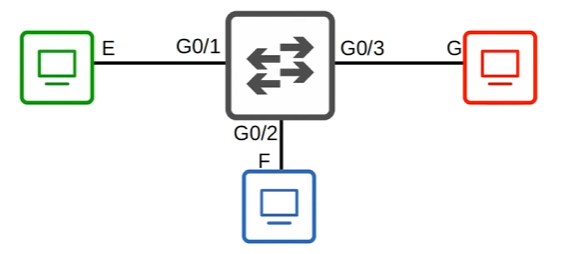
- E = 10 Mbps
- F = 10/100 Mbps
- G = 10/100/1000 Mbps
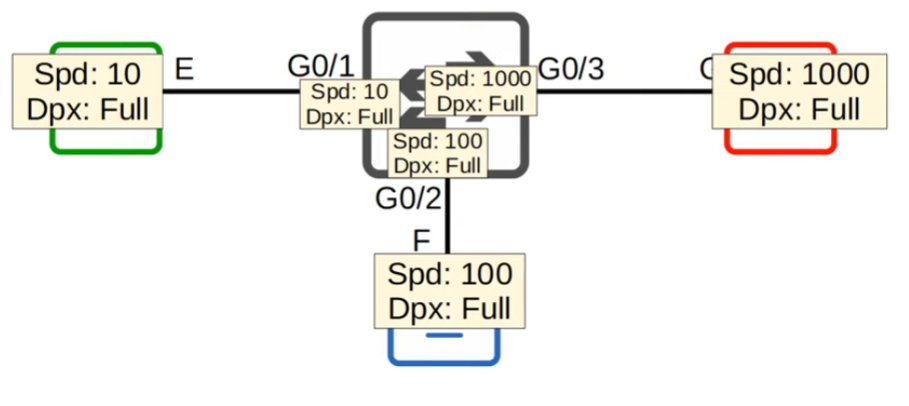
- G0/1 will negotiate to a speed of 10 Mbps and full duplex
- G0/2 will negotiate to a speed of 100 Mbps and full duplex
- G0/3 will negotiate to a speed of 1000 Mbps and full duplex
What if autonegotiation is disabled on the device connected to the switch ?
- SPEED
- The switch will try to sense the speed that the other device operating at 🔥
- if it fails to sense the speed, it will use the slowest supported speed. (i.e. 10 Mbps in a 10/100/1000 interface)
- DUPLEX
- If the speed is 10 or 100 Mbps, the switch will use half duplex 🔥🔥🔥
- if the speed is 1000 Mbps or greater, the switch will use full duplex 🔥🔥🔥
Interface Errors 🔥🔥🔥
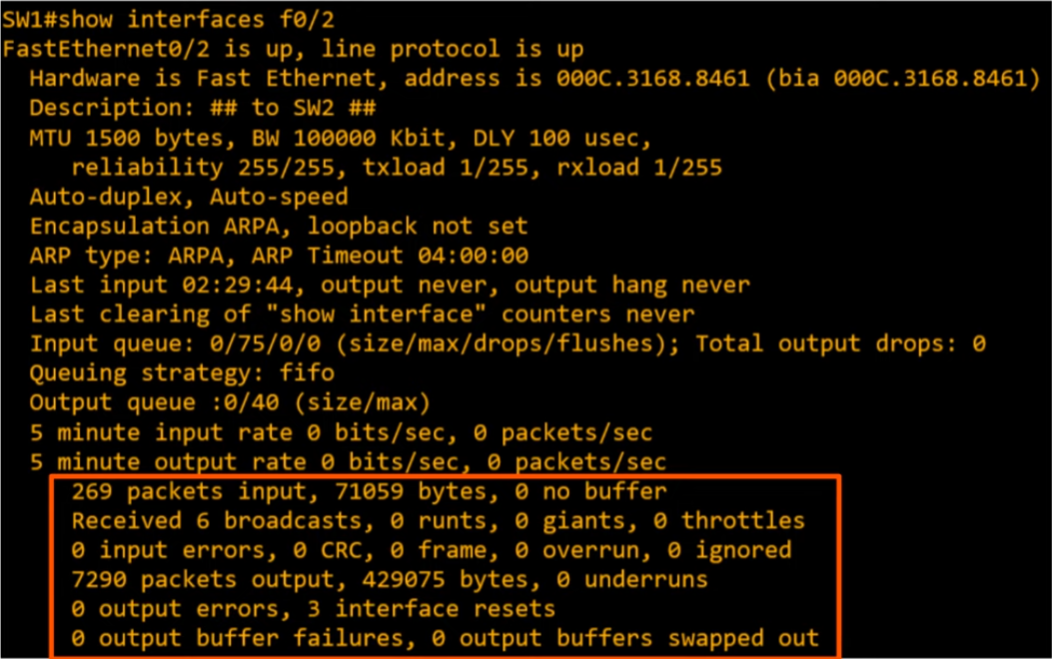
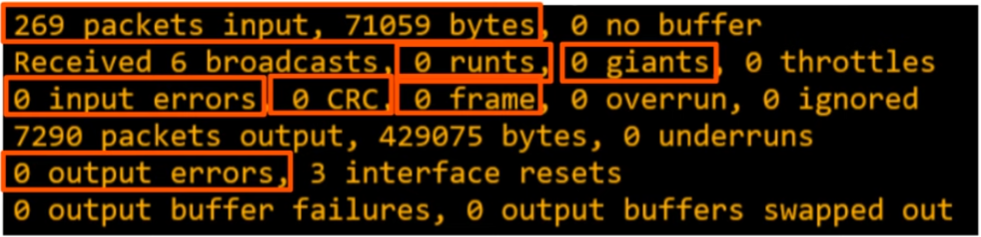
Runts: frames that are smaller than the minimum frame size of 64 bytesGiants: frames that are larger than the maximum frame size of 1518 bytesCRC: frames that failed the CRC check (in the ethernet FCS trailer)Frame: frames that have an incorrect format (due to an error)Input errors: total of various counters, such as the above fourOutput errors: frames the switch tried to send, but failed due to an error