system-design-refresher
Networking
For a more in-depth version you can see ccna-notes
Contents
- IP Addresses
- Internet Protocol
- Transport Layer
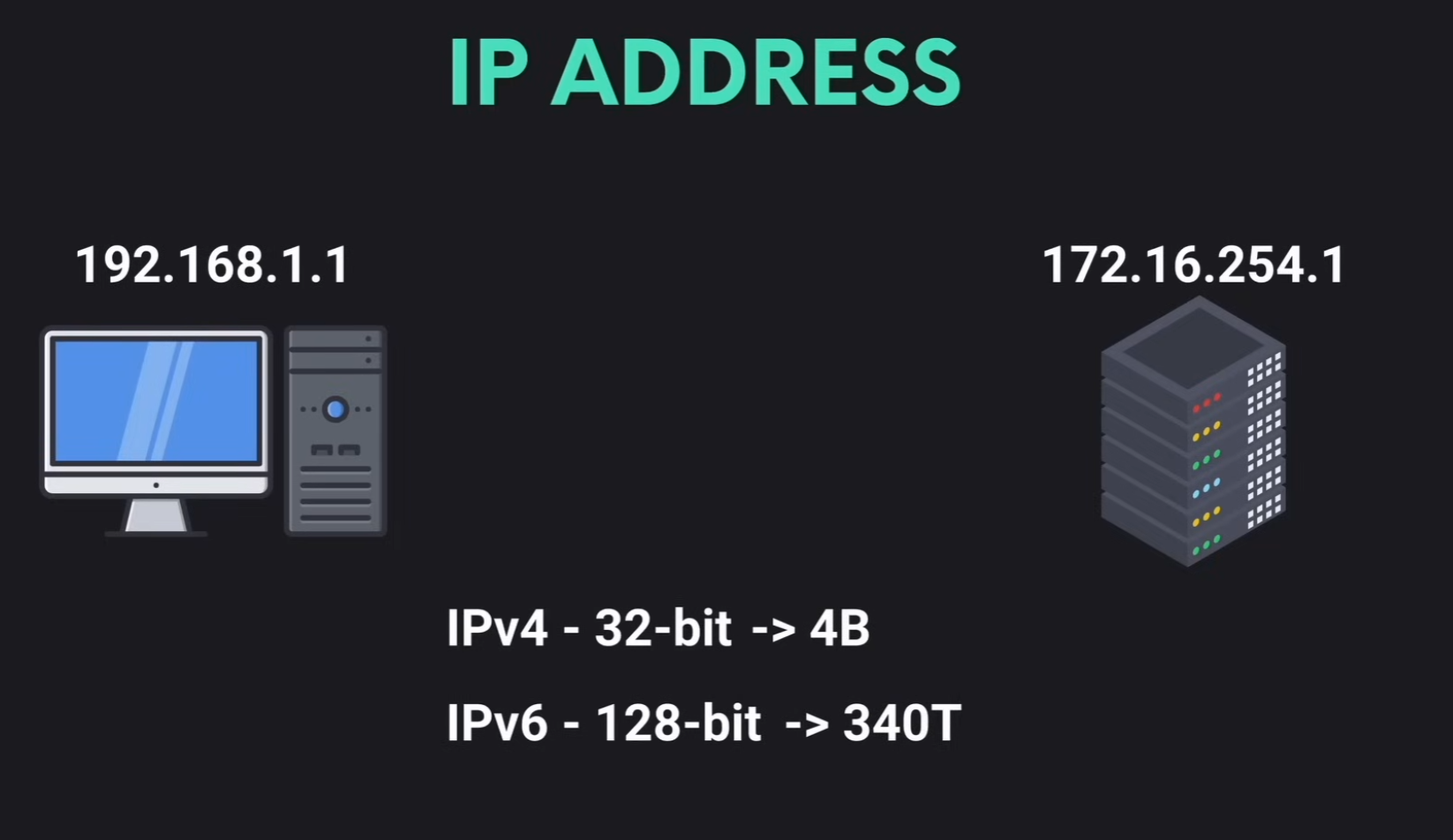
IP Address
A unique identifier for each device in a network.
IPv4addresses are 32bitIPv6addresses are 128bit significally increasing the number of available IP addresses
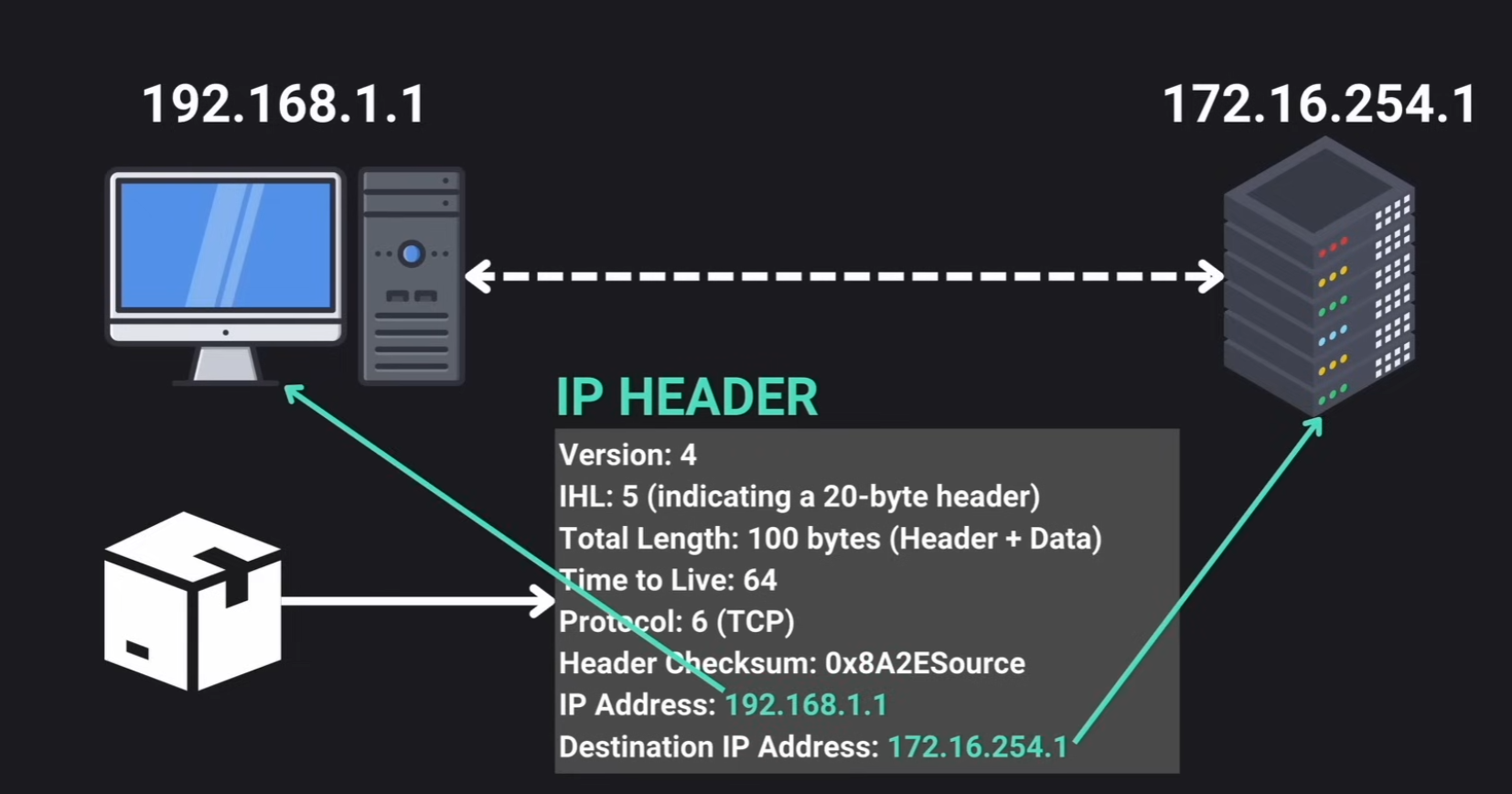
Internet Protocol
Set of rules that define how data is sent and received
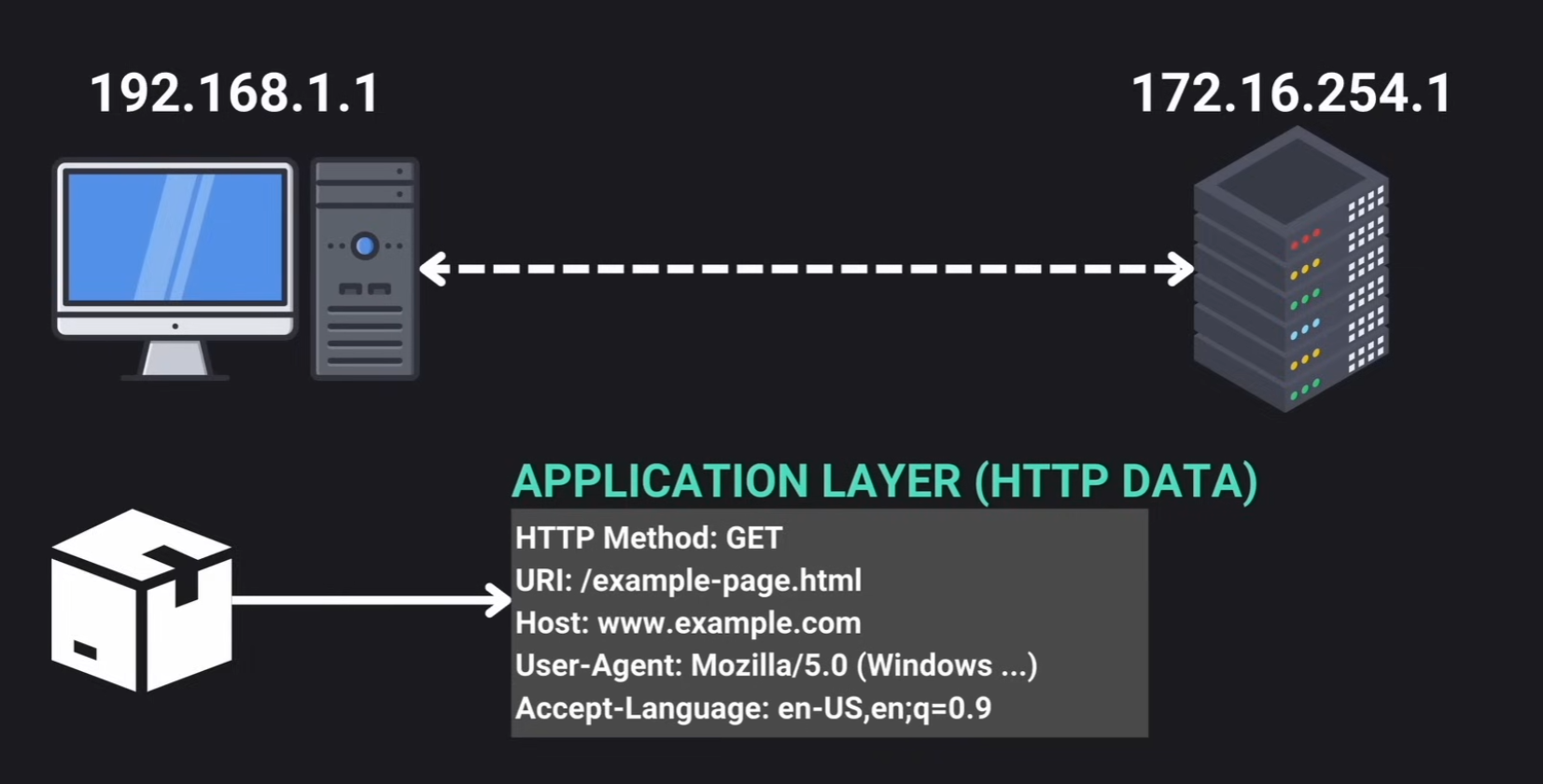
Application Layer
In this layer data specific to application protocol is stored.
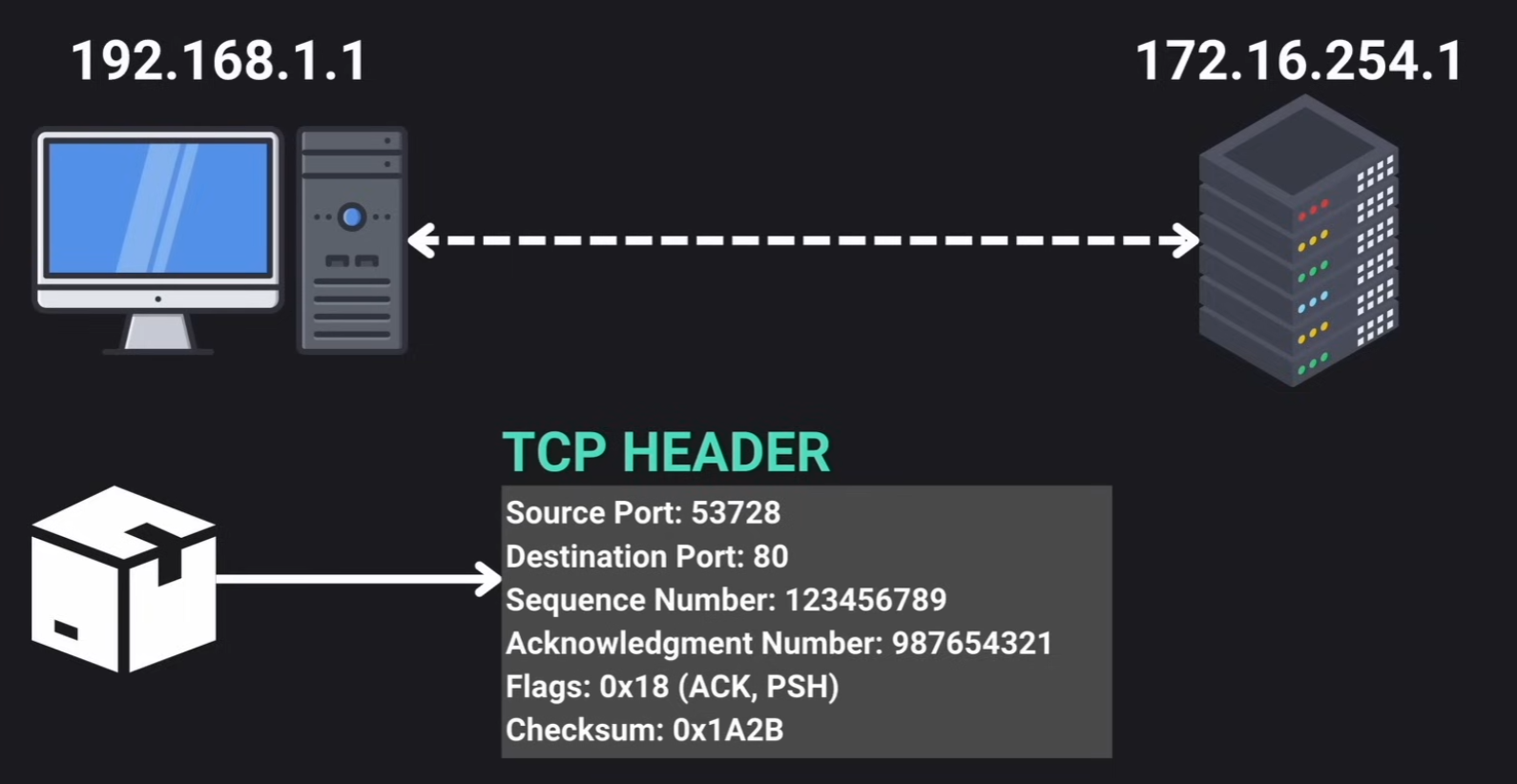
Transport Layer
TCP
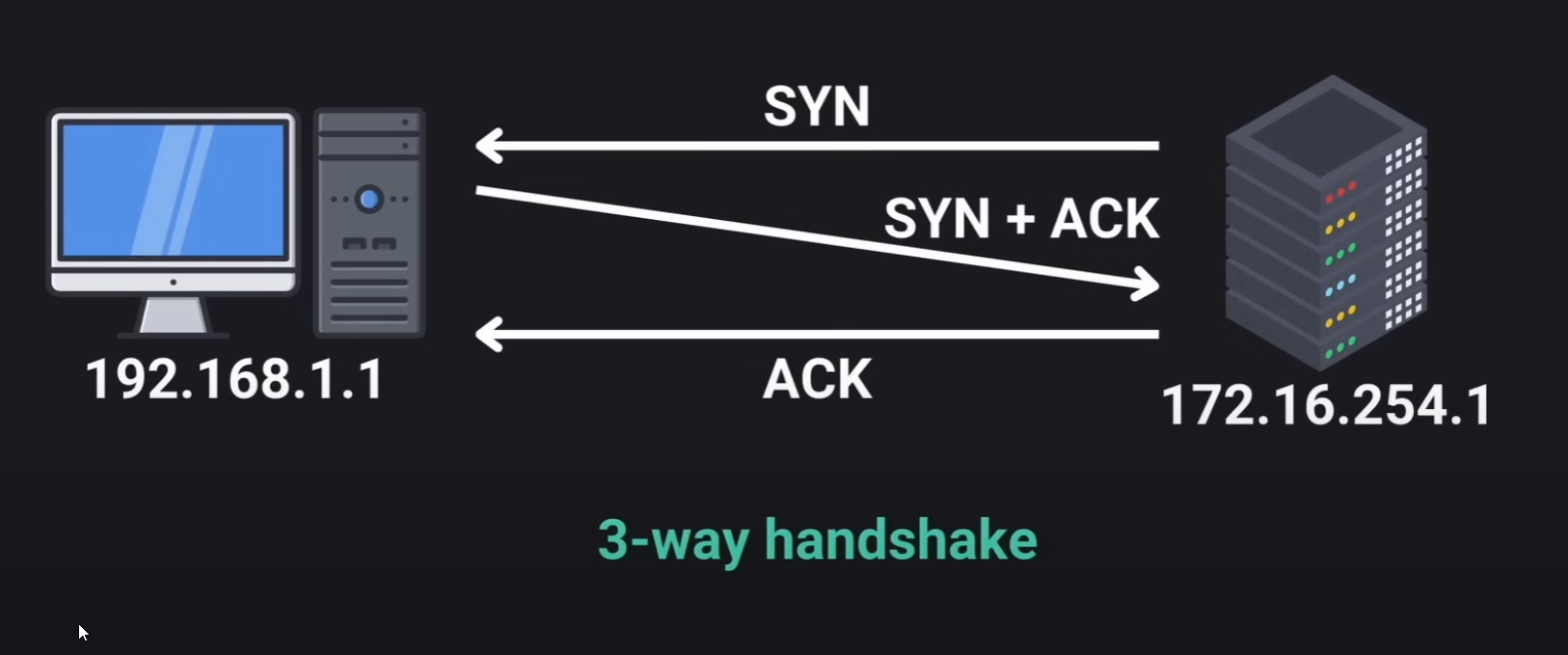
Transmission Control Protocol ensures complete and correct delivery of data packets. It implements a process known as 3-way handshake.
UDP
User Datagram Protocol is faster but less reliable than TCP. It doesn’t stablish a connection before sending data and doesn’t guarantee the delivery or order of the packages. Usually used for time-sensitive communications like video-calls or live-streaming where speed is crucial and some data loss is acceptable.
DNS
Domain Name System translates human-friendly domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to stablish a connection to the server and retrieve the web resource.
A Record: Maps the domain to the corresponding IPv4 AddressAAAA Record: Maps the domain to the corresponding IPv6 Address
ICANN
Coordinates the global IP address space and DNS. Domain name registrars are accredited by ICANN to sell domain names to the public.
Network Infrastructure
Devices connected in a LAN (Local Area Network) can communicate with each other directly.
Public vs Private IP Address
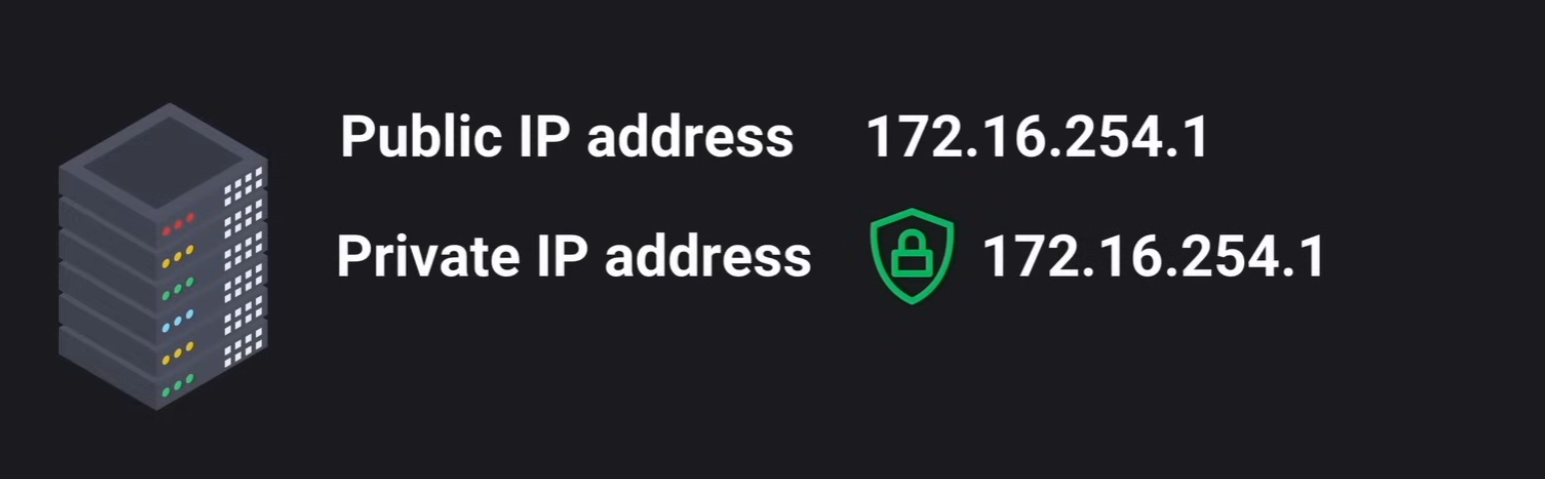
Public IP Address: unique across the internetPrivate IP Address: unique within the local network
Firewalls
We use firewalls to protect a network which monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Ports
Within a device specific processes are identified by ports. Some ports are reserved for specific protocols:
HTTP: 80HTTPS: 443SSH: 22